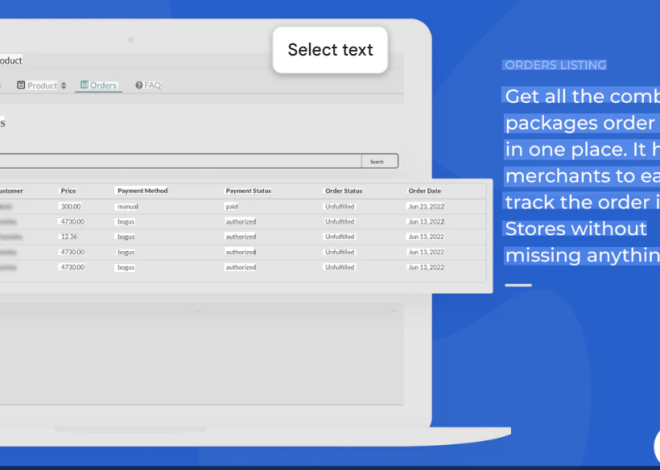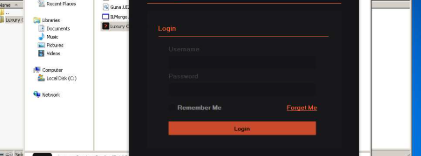
Acordx Crypter 2024 Cracked
In today’s cybersecurity landscape, Acordx Crypter 2024 are playing an increasingly significant role in enabling sophisticated cyberattacks. These tools are specifically designed to bypass modern security measures by disguising malicious code, making them a favourite among ransomware operators, data thieves, and other cybercriminals. Cracked or pirated versions of crypters circulating in underground forums further lower the barrier to entry, allowing even less-skilled attackers to deploy advanced evasion techniques. Security teams face an ongoing challenge in detecting these obfuscated threats, as crypters continuously evolve to defeat both signature-based and behavioural analysis systems.
This software is a powerful crypter that has been illicitly modified (cracked) to remove licensing restrictions, making it widely accessible to malicious actors. Its primary function is to transform detectable malware into fully undetectable (FUD) payloads that can evade antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and sandbox analysis. Attackers frequently use it to distribute information stealers, ransomware, and remote access trojans (RATS). While its cracked nature makes it unstable in some cases, its affordability in underground markets has led to widespread abuse in credential theft campaigns and targeted attacks.
Key Features of Acordx Crypter 2024
| Feature | Description |
| Runtime Encryption | Encrypts payloads in memory to avoid disk-based detection. |
| Anti-Debugging | Detects and blocks debugging tools, such as OllyDbg and x64dbg. |
| Process Doppelgänging | Leverages NTFS transactions to load malicious code without file drops. |
| API Obfuscation | Mask Windows API calls to evade behavioural analysis. |
| Dynamic Imports | Loads libraries at runtime to bypass static import analysis. |
| Sandbox Evasion | Checks for virtualized environments and delays execution in suspicious cases. |
How Acordx Crypter 2024 Works
The crypter employs a sophisticated multi-stage approach to ensure payload delivery while avoiding detection:
- Payload Transformation
- The original malware is first compressed and then encrypted using a combination of algorithms, including AES for core encryption and RC4 as a secondary layer.
- A custom packer then restructures the executable’s PE (Portable Executable) headers to break signature-based detection.
- Stub Generation & Anti-Analysis
- The encrypted payload is embedded into a polymorphic stub that changes its code patterns with each generation.
- Before execution, the stub performs multiple checks:
- Verifies the absence of debugging tools (using the IsDebuggerPresent API or hardware breakpoint detection)
- Tests for virtual machine artefacts (incorrect processor timing, known sandbox MAC addresses)
- Measures system uptime to detect short-lived sandbox sessions
- Stealth Execution
- Once in a clean environment, the stub employs Process Doppelgänging or Process Hollowing:
- Creates a legitimate process in a suspended state (e.g., notepad.exe)
- Replaces its memory space with the decrypted payload
- Resumes execution, making the malware appear as part of a trusted process
- For added stealth, critical API calls are resolved dynamically using hash-based lookups rather than direct imports.
- Once in a clean environment, the stub employs Process Doppelgänging or Process Hollowing:
- Persistence & Evasion
- The payload establishes persistence through:
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) event subscriptions
- Tamper-proof scheduled tasks configured with system-level privileges
- Hidden registry entries in non-standard locations
- Ongoing evasion is maintained by:
- Unhooking security product hooks from user-mode APIS
- Using direct system calls (syscalls) to bypass EDR monitoring
- Periodically checking for analysis tools and terminating if detected
- The payload establishes persistence through:
This combination of advanced obfuscation, anti-analysis techniques, and memory-based execution allows the crypter to deliver payloads that remain undetected for extended periods. Security solutions must rely on heuristic analysis, machine learning models, and in-memory scanning to identify such threats, as traditional detection methods prove increasingly ineffective against these evolving evasion tactics.