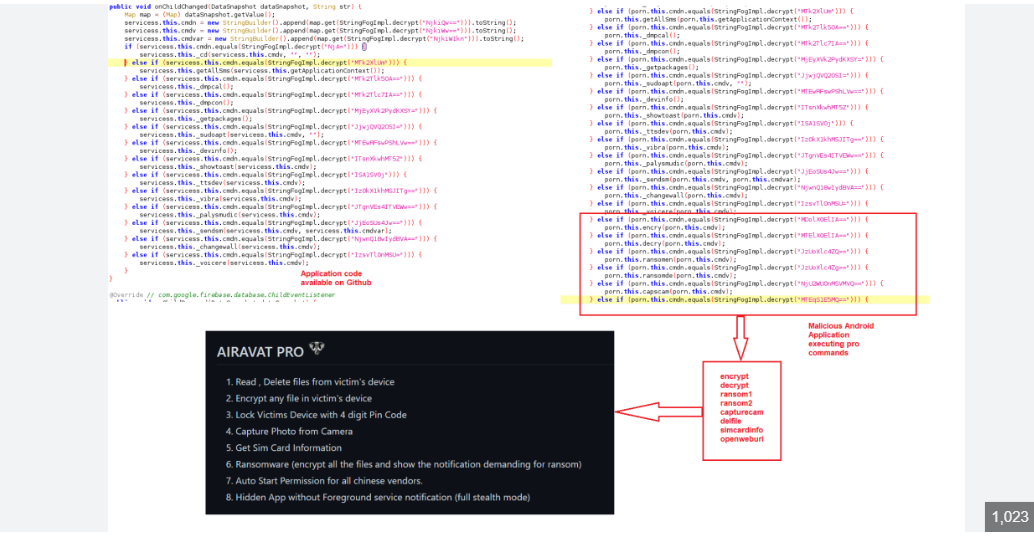
AIRAVAT multifunctional Android RAT 2025
Cybercriminals are increasingly using sophisticated Android Remote Access Trojans (RATs) to breach mobile devices, steal sensitive data, and maintain hidden control over their victims. AIRAVAT multifunctional Android malicious tools pose a severe risk due to their stealthy operation, modular capabilities, and ability to evade detection. Attackers leverage them in espionage, financial fraud, and large-scale botnet attacks, making them a persistent challenge for cybersecurity defenses.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
This Android-based remote access malware operates as a powerful, multifunctional tool for attackers. Cybercriminals distribute it through phishing scams, fake app stores, or trojanized applications disguised as legitimate software. Once installed, it grants full device control, enabling data theft, real-time surveillance, and further malware deployment. Its adaptability makes it useful for various malicious purposes, from corporate spying to banking fraud.
Key Features of AIRAVAT multifunctional Android
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote Access | Attackers remotely control the infected device, allowing them to access files and execute commands. |
| Keylogging | The malware logs every keystroke, capturing passwords, credit card details, and private messages. |
| Camera & Mic Access | Hackers secretly activate the camera and microphone to spy on victims. |
| Data Theft | The RAT steals contacts, call logs, SMS, and sensitive documents from the device. |
| Persistence | It embeds itself deeply into the system, surviving reboots and resisting removal. |
| Payload Delivery | The malware downloads and executes additional malicious modules, such as ransomware or spyware. |
| Anti-Detection | It uses encryption, obfuscation, and process hiding to avoid security scans. |
How AIRAVAT multifunctional Android
Infection and Initial Compromise
Attackers deliver the malware through:
Fake apps (disguised as games, utilities, or system updates).
Phishing links (tricking users into downloading malicious APKs).
Exploiting vulnerabilities (in Android or outdated apps to gain access silently.
Once installed, the malware hides its presence while establishing a connection to the attacker’s server.
Core Attack Techniques
Maintaining Persistence
The malware disguises itself as a system service or critical app process.
It abuses device administrator permissions to prevent uninstallation.
Command & Control (C2) Communication
The infected device connects to a remote server controlled by hackers.
All communications use encryption to bypass firewalls and detection tools.
Dynamic Payload Execution of the AIRAVAT multifunctional Android
Attackers send commands to deploy additional malware, such as:
Spyware (for real-time tracking).
Ransomware (to encrypt files and demand payment).
Banking Trojans (to steal financial credentials).
Data Harvesting & Exfiltration
The malware collects:
SMS/call logs
GPS location
Authentication tokens (for account takeovers)
It sends stolen data in encrypted packets to the attacker’s server.
Evading Detection
Code obfuscation – Makes reverse-engineering difficult.
Process impersonation – Mimics legitimate apps to avoid suspicion.
Killing security apps – Actively disables antivirus or monitoring tools.


