Carding and Hacking Tools 2024
Cyberattacks continue to evolve in sophistication, leveraging advanced tools to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. Among these tools, carding and hacking software has become a significant threat, enabling malicious actors to conduct financial fraud, data breaches, and unauthorized access at scale. The “Carding and Hacking Tools 2024” category represents a collection of modernized utilities designed to automate attacks, bypass security measures, and exfiltrate sensitive information. These tools are frequently distributed through underground forums and pose a serious risk to individuals, businesses, and financial institutions.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
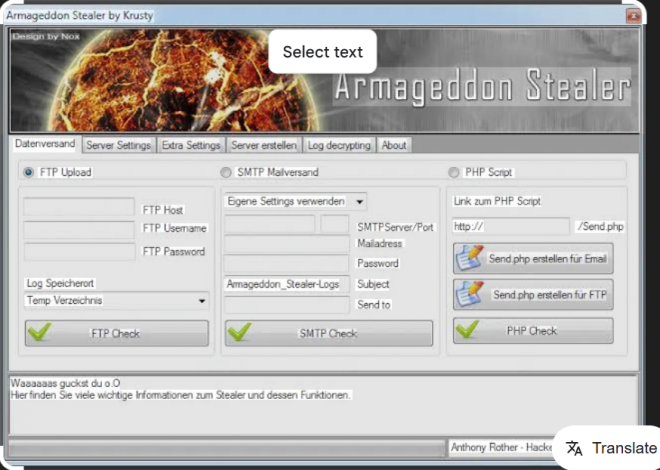
This software is a multi-functional toolkit primarily used for illicit activities such as credit card fraud (carding), credential theft, and system infiltration. It typically includes features such as automated brute-forcing, phishing kit integration, and proxy support to conceal the attacker’s identity. Cybercriminals deploy it to exploit weak authentication mechanisms, harvest payment card data, and deliver malicious payloads. While its capabilities vary, the software is often modular, allowing users to customize attacks based on their objectives.
Key Features of Carding and Hacking
Below is a table summarizing the core functionalities of the software:
| Feature | Description |
| Automated Carding | Test stolen credit card details against payment gateways for validity. |
| Brute-Force Attack Tools | Attempts multiple password combinations to gain unauthorized access. |
| Phishing Kit Integration | Deploys fake login pages to steal credentials or financial data. |
| Proxy and VPN Support | Route traffic through intermediaries to evade IP-based detection. |
| Exploit Delivery | Leverages known vulnerabilities to execute remote code or install malware. |
| Data Scraping | Extracts sensitive information from compromised systems or websites. |
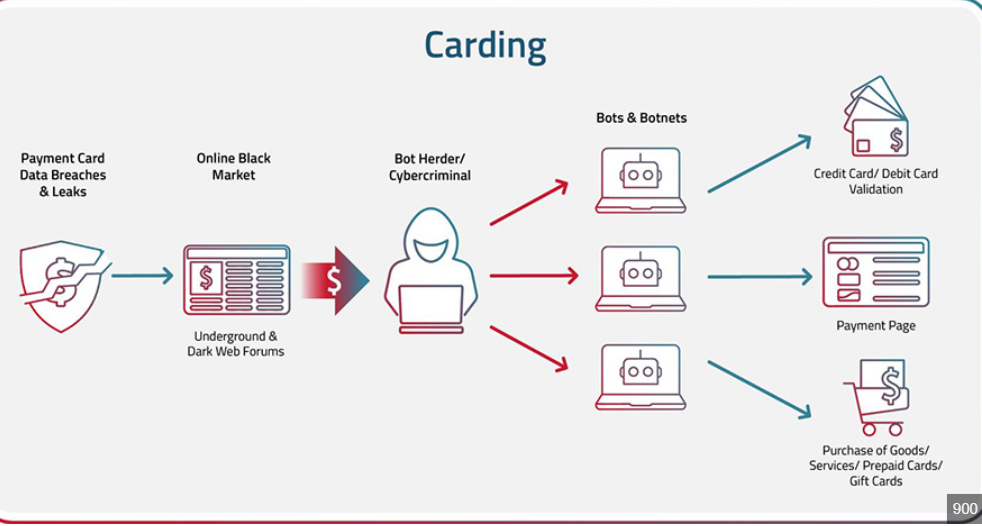
How Carding and Hacking Work
The software operates through a combination of automation, evasion techniques, and exploitation methods. Below is a breakdown of its functionality:
Reconnaissance and Target Selection
The tool scans for vulnerable systems or websites, often using automated scripts to identify weak points such as outdated software, misconfigured databases, or exposed APIs.Attack Execution
- Brute-Forcing & Credential Stuffing: Uses wordlists or previously leaked credentials to gain access to accounts or systems.
- Phishing: Deploys spoofed websites or emails to trick victims into entering sensitive data, which is then captured.
- Carding Automation: Tests batches of stolen card details against e-commerce sites or payment processors to verify active cards.
Payload Delivery
If malware deployment is part of the attack, the software may use:
- Exploit Kits: Leverage known vulnerabilities (e.g., in browsers or plugins) to silently install malware.
- Social Engineering: Tricks users into executing malicious files disguised as legitimate software.
Evasion Techniques of Carding and Hacking
To avoid detection, the tool employs:
- Proxy Chaining: Routes traffic through multiple proxies or Tor to obscure the attacker’s origin.
- Encryption: Encrypts exfiltrated data to prevent interception.
- Anti-Sandboxing: Detects virtualized environments (e.g., sandboxes) and halts execution to evade analysis.
Exfiltration & Monetization
Stolen data is either sold on dark web marketplaces or used directly for fraudulent transactions. The software may include built-in mechanisms to automate data transfers to attacker-controlled servers.