CHAOS RANSOMWARE 2025
Ransomware has emerged as one of the most destructive and financially motivated cyber threats in recent years, with attackers constantly refining their tactics to maximize impact. The latest generation of CHAOS RANSOMWARE 2025 variants demonstrates increased sophistication, combining advanced encryption methods with aggressive propagation techniques. These malicious programs have evolved beyond simple file encryption to include data exfiltration, system sabotage, and even triple-extortion tactics. The growing prevalence of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) models has lowered the barrier to entry, enabling less technical criminals to deploy devastating attacks against businesses, critical infrastructure, and individuals worldwide.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
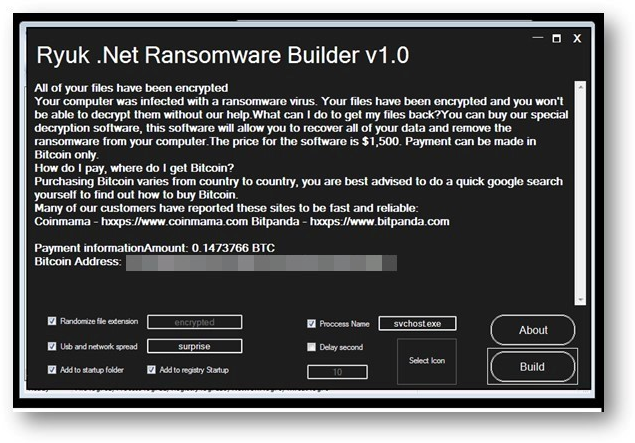
This ransomware variant represents a significant evolution in malicious encryption technology, designed to encrypt files while systematically evading modern security measures. It typically infiltrates systems through phishing campaigns, exploit kits, or compromised remote desktop connections. Once activated, it employs military-grade encryption algorithms to lock files across local drives, network shares, and cloud storage connections. What sets this variant apart is its additional functionality for data theft before encryption, enabling attackers to demand payment not just for file recovery, but also to prevent public release of sensitive information. The malware includes self-propagation mechanisms, allowing it to spread rapidly across networked environments.
 Key Features
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Hybrid Encryption | Combines AES-256 and RSA-4096 for unbreakable file encryption. |
| Data Exfiltration | Steals sensitive files before encryption for double-extortion leverage. |
| Network Propagation | Spreads automatically to connected systems via SMB and RDP vulnerabilities. |
| Process Termination | Kills security software, database, and backup processes before encryption. |
| Persistent Access | Establishes a backdoor for follow-up attacks even after ransom payment. |
| Custom Ransom Notes | Generates personalized ransom demands with victim-specific information. |
| Anti-Analysis | Detects and halts execution in sandboxes or virtual machine environments. |
How CHAOS RANSOMWARE 2025 Works
Initial Infection and Execution
The ransomware typically gains access through:
- Phishing Emails: Malicious attachments or links delivering the payload
- Exploit Kits: Targeting unpatched vulnerabilities in software or operating systems
- Brute Force Attacks: Compromising weak RDP or VPN credentials
- Supply Chain Attacks: Bundled with legitimate software updates or installers
Upon execution, the malware performs several preparatory steps:
- System Reconnaissance: Gathers information about the environment, including:
- Network topology and connected systems
- Installed security software
- Available drives and file shares
- Persistence Mechanisms: Establishes multiple persistence methods:
- Registry modifications (e.g., Run keys)
- Scheduled tasks for reactivation
- Creation of new service entries
Encryption Process
The ransomware employs a sophisticated multi-stage encryption approach:
- Key Generation: Creates unique encryption keys for each victim
- File Targeting: Selects files based on predefined extensions (documents, databases, backups)
- Process Termination: Stops critical services and applications to prevent file locking issues
- Encryption Routine:
- Uses fast symmetric encryption (AES-256) for file contents
- Protects AES keys with asymmetric encryption (RSA-4096)
- Appends custom file extensions to encrypted files
- Shadow Copy Deletion: Removes Volume Shadow Copies to prevent easy recovery
Data Exfiltration
Before encryption, the malware:
- Identifies valuable data based on file types and locations
- Compresses and encrypts stolen files for exfiltration
- Transfers data to attacker-controlled servers using:
- HTTPS for small datasets
- FTP or cloud storage APIs for larger transfers
Ransom Demand and Communication
The malware leaves customized ransom notes containing:
- Instructions for payment (typically in cryptocurrency)
- The threat of data leakage if payment is not made
- Unique victim ID for communication
- Deadline with increasing ransom amounts
Communication occurs through:
- TOR-based payment portals
- Encrypted email services
- Anonymous chat platforms
Evasion Techniques
To avoid detection and analysis, the ransomware employs:
- Polymorphic Code: Changes its signature with each infection
- Process Injection: Runs within legitimate system processes
- Sandbox Detection: Checks for virtualized environments before executing
- Network Traffic Obfuscation: Uses DNS tunneling or common cloud services for C2


