Cpanel Checker Account 2025
As web hosting control panels remain critical infrastructure for millions of websites, specialized tools have emerged to target these administrative interfaces. In 2025, credential testing tools focusing specifically on hosting control panels have become increasingly sophisticated, posing significant risks to web infrastructure security. These tools enable attackers to systematically probe for vulnerable accounts, often serving as the initial entry point for more severe compromises, including website defacement, malware distribution, and data theft. Cpanel Checker Account 2025’s role in modern cyberattacks has expanded due to the high value of compromised hosting accounts, which can provide attackers with persistent access to multiple websites and server resources. The automation and precision of these tools have made them particularly dangerous, allowing attackers to scale their operations while evading basic security measures.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
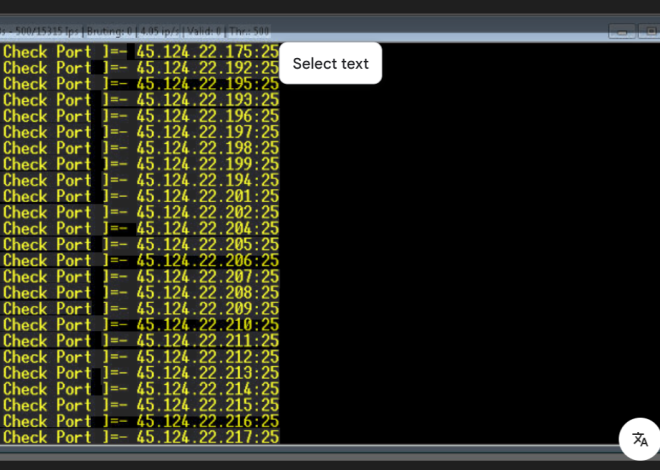
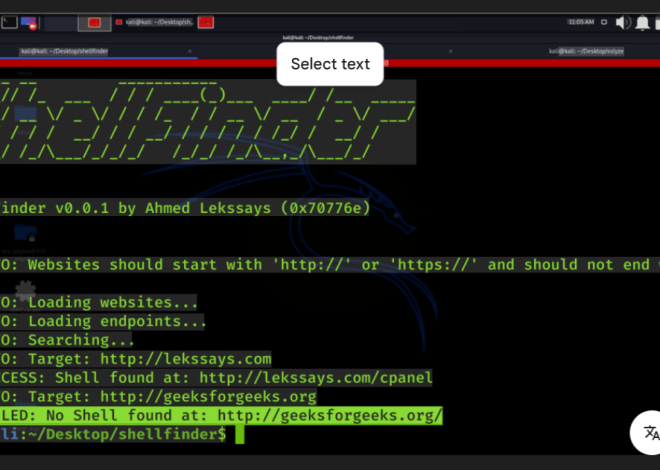
This specialized tool is designed to automate the testing of credentials against web hosting control panels, with particular focus on the most widely used administration interfaces. It functions as a targeted credential stuffing platform, combining protocol-specific knowledge with advanced evasion techniques to enhance its effectiveness. While system administrators may use similar tools for security audits, attackers typically deploy this software to identify hosting accounts that are poorly secured and can be compromised. The software’s effectiveness stems from its in-depth understanding of control panel authentication mechanisms and its ability to mimic legitimate administrator traffic, enabling it to bypass basic security protections while efficiently testing large volumes of credentials.

Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Control Panel Detection | Automatically identifies hosting control panel versions and types |
| Protocol-Specific Testing | Optimized authentication testing for various control panel implementations |
| Session Hijacking | Captures and reuses authenticated sessions after successful logins |
| Proxy Chaining | Rotates through multiple proxy layers to avoid IP blocking |
| Two-Factor Bypass | Attempts to circumvent common 2FA implementations |
| Vulnerability Scanning | Checks for known vulnerabilities in the control panel software |
| Bulk Processing | Handles large credential lists with configurable threading |
| Detailed Reporting | Generates comprehensive logs of successful compromises and vulnerabilities |
How Cpanel Checker Account 2025 Works
- Target Acquisition and Initialization
- Accepts input as domain lists, IP ranges, or specific server addresses
- Automatically detects hosting control panels through:
- Default URL paths
- Characteristic response headers
- SSL certificate analysis
- Fingerprints control panel version and configuration
- Credential Testing Process
- For each credential pair:
- Routes connection through the proxy network
- Loads the login page with proper headers and cookies
- Submits credentials using correct form fields and protocols
- Analyzes responses for authentication success indicators
- Handles security challenges and redirects
- Uses control panel-specific techniques:
- Proper sequence of authentication requests
- Required hidden form fields
- Expected HTTP headers
- Session Establishment and Validation
- For successful logins:
- Captures session cookies and tokens
- Verifies access level and privileges
- Screenshots administrative interface
- Checks for multi-website management capabilities
- Advanced Exploitation
- Automated reconnaissance of compromised accounts:
- Website inventories
- Database access credentials
- SSL certificate management
- Privilege escalation attempts:
- Root access probing
- API key extraction
- Backup file access
- Payload Delivery
- Website compromises:
- Malicious file uploads
- Code injection
- Defacement templates
- Backdoor installation:
- Web shells
- Cron job persistence
- Hidden administrator accounts
- Data exfiltration:
- Database dumps
- Email account access
- Configuration file theft
- Evasion Techniques
- Traffic randomization:
- Variable timing between attempts
- Mixed case request headers
- Randomized URL parameters
- IP reputation management:
- Residential proxy rotation
- Cloud service IP blending
- Geographic consistency
- Post-Compromise Activities
- Maintains access through:
- Control panel backdoors
- SSH key injection
- Database triggers
- Monitors for administrator activity
- Covers tracks by modifying logs