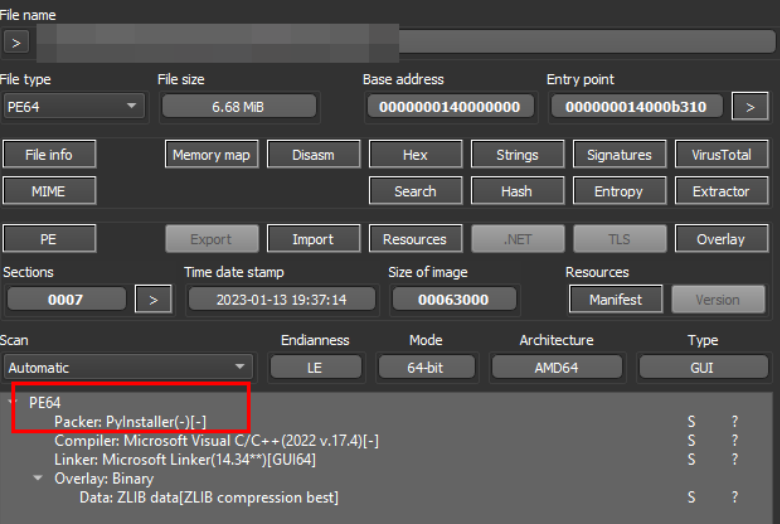
CREAL STEALER 2025
Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging advanced information-stealing malware to compromise sensitive data, and one such prominent threat is “CREAL STEALER 2025.” This malware exemplifies the growing sophistication of modern cyberattacks, targeting credentials, financial data, and other valuable information from infected systems. Unlike generic stealers, this tool employs evasion techniques to avoid detection while efficiently exfiltrating data to attacker-controlled servers. Its modular design and adaptability make it a persistent threat in both individual and enterprise-level breaches.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
The software is a type of malware designed to harvest sensitive information from compromised systems. It primarily targets login credentials, browser-stored data, cryptocurrency wallets, and system information. Typically distributed through phishing campaigns, malicious downloads, or exploit kits, the malware operates stealthily to avoid triggering security defences. Cybercriminals often use it as part of a broader attack chain, selling stolen data on underground markets or leveraging it for further exploitation.
Key Features of CREAL STEALER 2025
| Feature | Description |
| Credential Harvesting | Extracts saved logins from browsers and applications. |
| Cookie Theft | Steals session cookies to bypass authentication. |
| Form Grabbing | Captures input from web forms in real time. |
| Cryptocurrency Targeting | Scans for and exfiltrates wallet files and keys. |
| Anti-Detection Mechanisms | Uses obfuscation, encryption, and sandbox evasion techniques. |
| Data Exfiltration | Sends stolen data to C2 (Command & Control) servers via HTTPS or Tor. |
| Persistence | Establishes auto-start mechanisms to survive reboots. |
How CREAL STEALER 2025 Works
Infection and Execution
The malware typically infiltrates systems through deceptive means, such as malicious email attachments, fake software installers, or compromised websites. Once executed, it may deploy a dropper to unpack and install the core-stealing module. To evade detection, the payload may be encrypted or split into smaller components, only reassembling in memory.
Data Collection Techniques
The stealer employs several methods to gather sensitive information:
- Browser Targeting: It scans popular browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge) for stored credentials, cookies, and autofill data.
- System Reconnaissance: Collects system details (OS, hardware, installed software) to identify high-value targets.
- File Scanning: Searches for documents, cryptocurrency wallets, and configuration files in specific directories.
- Keylogging (Optional): Some variants log keystrokes to capture additional credentials.
Evasion and Persistence of CREAL STEALER 2025
To avoid detection, the malware may:
- Terminate security processes.
- Disable firewall rules.
- Use process hollowing (injecting malicious code into legitimate processes).
For persistence, it may create scheduled tasks, registry entries, or hidden startup scripts.
Data Exfiltration
Stolen data is compressed, encrypted, and transmitted to a C2 server using secure channels like HTTPS or Tor. Some variants employ decentralized storage (e.g., Telegram bots or cloud services) to conceal the attacker’s infrastructure.
Post-Exploitation
Attackers analyze the stolen data for monetization, either through direct use (e.g., financial fraud) or resale on dark web forums. In some cases, the malware may download additional payloads, such as ransomware or remote access trojans (RATS), for further exploitation.
By combining these techniques, the malware efficiently compromises systems while maintaining a low profile, making it a significant threat in today’s cybersecurity landscape.


