EdgeGuard Stealer 2025
Cybercriminals continually evolve their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities and steal sensitive data, with information-stealing malware playing a significant role in modern cyberattacks. One such example is a sophisticated stealer that emerged in 2025, designed to harvest credentials, financial data, and other valuable information from compromised systems.EdgeGuard Stealer 2025 stealers are distributed through phishing campaigns, malicious downloads, or exploit kits, enabling attackers to monetize the stolen data on underground markets or use it for further attacks, such as ransomware or identity theft.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
This type of malware is a specialized data-stealing tool that targets browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, installed applications, and system information. It operates stealthily to avoid detection while exfiltrating sensitive data to a command-and-control (C2) server. Typically, it is used by threat actors to gather intelligence for financial fraud, corporate espionage, or credential-stuffing attacks.
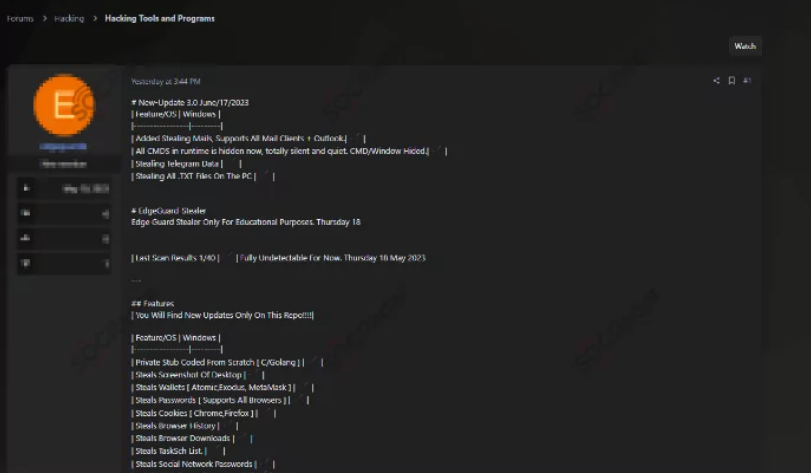
Key Features of EdgeGuard Stealer 2025
| Feature | Description |
| Browser Data Extraction | Harvests saved passwords, cookies, and autofill data from multiple browsers. |
| Cryptocurrency Theft | Targets wallet files and clipboard data to hijack transactions. |
| System Information Logging | Collects OS details, hardware specs, and network configurations. |
| Anti-Detection Mechanisms | Uses obfuscation, process injection, and sandbox evasion to avoid AV detection. |
| C2 Communication | Encrypts and transmits stolen data to a remote server via HTTPS or custom protocols. |
| Persistence | Establishes registry modifications or scheduled tasks to maintain access. |
How EdgeGuard Stealer 2025 Works
1. Infection and Execution
Attackers typically deliver EdgeGuard Stealer 2025 through malicious email attachments, fake software installers, or compromised websites. Once a victim executes the file, the malware initiates its infection chain using several stealthy techniques.
Dropper Phase: The attacker often hides the initial payload inside a harmless-looking executable or document macro. When triggered, this dropper extracts the core stealer module into memory or a temporary folder and executes it.
Persistence Mechanisms: To maintain access, the malware sets up scheduled tasks, modifies registry keys, or installs itself as a Windows service, ensuring it runs even after system reboots.
2. Data Harvesting Techniques
After establishing persistence, EdgeGuard Stealer begins scanning the system to harvest sensitive information from specific targets:
Browser Data: The stealer extracts login credentials, cookies, and session tokens from browser profiles, with a focus on Chrome, Firefox, and Edge.
Cryptocurrency Wallets: It hunts for wallet files and monitors the clipboard for cryptocurrency addresses, enabling it to hijack transactions by swapping copied addresses.
Installed Applications: The malware pulls saved credentials from FTP clients, messaging apps, and other software that store sensitive user data.
System Information: It logs details like IP addresses, operating system versions, and installed antivirus software to help attackers tailor future exploitation efforts.
3. Payload Delivery and Exfiltration
Once it collects the stolen data, the malware compresses and encrypts the files before initiating the exfiltration process:
HTTPS Requests: It disguises the data transmission as normal encrypted web traffic to avoid detection by network monitoring tools.
Custom Protocols: Some variants use unusual ports or custom communication protocols to bypass traditional firewall rules.
Fallback Mechanisms: If it fails to reach the primary command-and-control (C2) server, EdgeGuard uses backup servers or stores the data locally until it can transmit it.
4. Anti-Analysis and Evasion
EdgeGuard employs multiple strategies to remain undetected and resist analysis:
Code Obfuscation: It scrambles its code to make reverse engineering and static analysis more difficult.
Process Hollowing: The malware injects its malicious code into legitimate processes to camouflage its activity.
Sandbox Detection: Before executing its core functionality, it checks for signs of debugging tools or virtual machines and delays or halts execution if detected.


