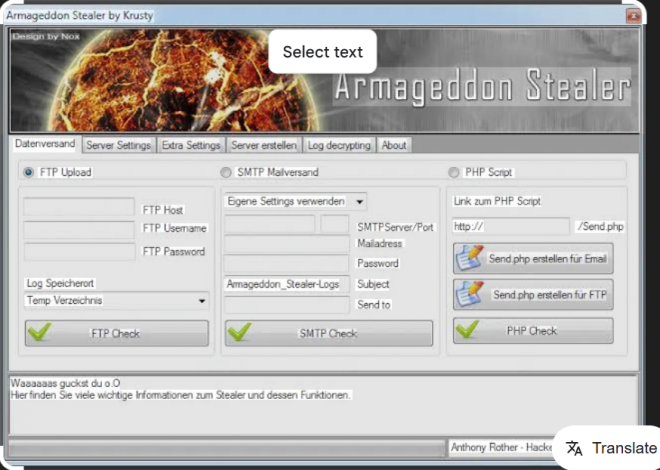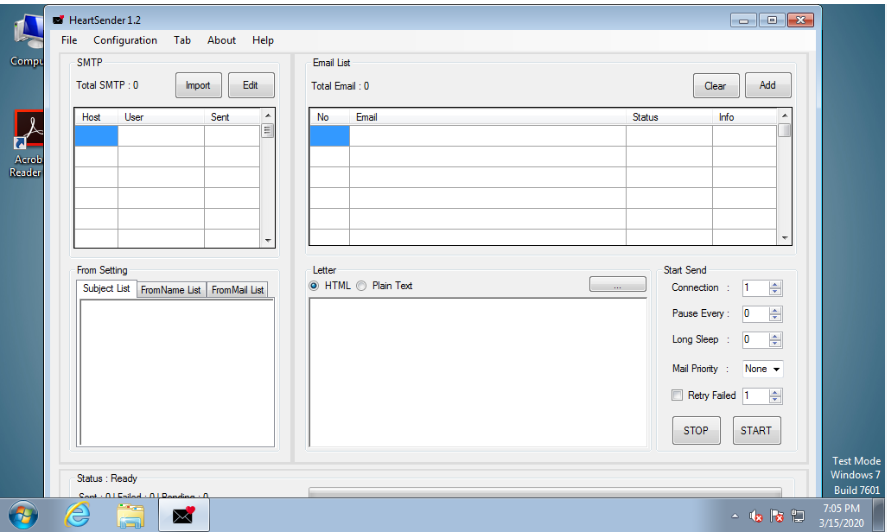
Heart Sender 3.0 Cracked
Cybercriminals are increasingly relying on cracked versions of legitimate tools to carry out sophisticated attacks, thereby evading detection while exploiting the powerful functionalities of these tools. One such example is Heart Sender 3.0 Cracked, a modified version of a commercial email marketing tool that has been repurposed for malicious campaigns. These cracked tools often bypass licensing restrictions and security checks, enabling threat actors to conduct large-scale phishing, spam, or malware distribution campaigns. Their use in modern cyberattacks underscores the risks associated with pirated software, which may contain hidden payloads or backdoors, thereby further compromising victims’ systems.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
The original software is designed for bulk email marketing, allowing businesses to send personalized messages to large contact lists. However, the cracked version is frequently weaponized by attackers to distribute malicious attachments, phishing links, or embedded scripts. Unlike legitimate use cases, which focus on engagement metrics and deliverability, the cracked variant prioritizes stealth, evasion, and payload execution.
Key Features of Heart Sender 3.0 Cracked
| Feature | Description |
| Template Customization | Pre-designed email templates for convincing phishing campaigns. |
| SMTP Integration | Supports multiple SMTP servers to bypass email provider restrictions. |
| Attachment Handling | Allows embedding malicious files (e.g., PDFS, Word docs) with macros. |
| Spoofing Capabilities | Manipulates sender headers to impersonate trusted entities. |
| Analytics Tracking | Log open rates and click-through rates to refine attack strategies. |
How Heart Sender 3.0 Cracked Works
The cracked tool operates in stages, combining social engineering with technical evasion techniques. Below is a breakdown of its functionality:
Campaign Setup
Attackers configure the email content and sender details, as well as those of the recipient organisations, to mimic legitimate organisations (e.g., banks, corporate vendors) and increase credibility.
Payload Delivery
Malicious payloads are attached or linked within the email. Common techniques include:
- Macro-Enabled Documents: Files that prompt users to enable macros, potentially triggering malware execution.
- Shortened URLs: Redirecting to phishing pages or drive-by download sites.
- Cloud Storage Links: Hosting malicious executables on compromised or public cloud platforms.
Evasion Techniques
- SMTP Rotations: The software cycles through different SMTP servers to avoid blocklisting.
- Dynamic Content: Emails adjust content based on recipient metadata (e.g., name, location) to appear authentic.
- Delay Scheduling: Staggered email sends reduce the likelihood of triggering spam filters.
Post-Delivery Actions
Once a victim interacts with the payload, the software may:
- Execute malware (e.g., ransomware, info-stealers) via dropped executables.
- Harvest credentials through fake login pages.
- Establish persistence by creating scheduled tasks or registry entries.