Improved RedLine Clipper 2025 Cracked
In the ever-evolving world of cybercrime, attackers are constantly refining their tools to exploit digital transactions, particularly those involving cryptocurrencies. One of the most insidious threats to emerge in recent years is an advanced form of malware designed to hijack cryptocurrency transfers by manipulating clipboard data. This sophisticated evolution of traditional Improved RedLine clipper 2025 malware has become increasingly prevalent in cyberattacks, targeting both individual investors and organizations conducting crypto transactions. Its ability to operate stealthily while causing direct financial losses makes it a particularly dangerous threat in today’s digital economy.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4

Overview of the Improved RedLine Clipper 2025
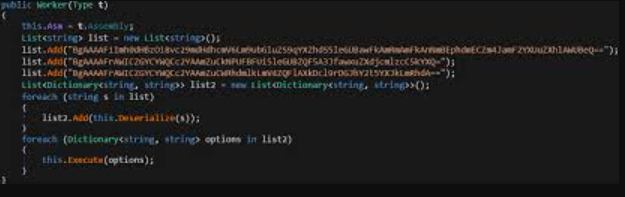
Improved RedLine Clipper 2025 software is a specialized form of malware that monitors and modifies clipboard contents to redirect cryptocurrency transactions. Unlike basic clippers that simply replace wallet addresses, this enhanced version incorporates multiple evasion techniques and expanded functionality to maximize its success rate. It primarily targets Windows systems and is typically distributed through pirated software, fake cryptocurrency tools, or malicious email attachments. Once installed, it runs silently in the background, waiting for users to copy and paste cryptocurrency addresses before substituting them with attacker-controlled addresses. The malware is particularly dangerous because it requires no additional action from victims after the initial infection—the attack occurs automatically during normal transaction behavior.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Smart Address Detection | Identifies cryptocurrency addresses in clipboard data with high accuracy |
| Multi-Currency Support | Targets Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other major cryptocurrencies |
| Dynamic Address Switching | Rotates between multiple attacker wallets to avoid detection |
| Transaction Monitoring | Tracks successful hijacks and reports to C2 server |
| Process Injection | Hooks into legitimate processes to evade detection |
| Anti-Analysis Checks | Detects and exits in virtualized or monitored environments |
| Persistence | Maintains access through registry modifications or task scheduling |
| Geofencing | Only activates in targeted geographical regions |
How the Software Works
The malware employs a sophisticated multi-stage approach to ensure successful operation while avoiding detection:
1. Delivery and Infection
- Trojanized cryptocurrency apps.
- Pirated software bundles.
- Malicious email attachments.
2. Installation and Persistence
- Creating registry autorun entries for persistence.
- Setting up Windows scheduled tasks for regular execution.
- Implementing process hollowing to inject into legitimate applications.
- Using fileless techniques to minimize disk footprint.
3. Clipboard Monitoring
- Continuous clipboard monitoring.
- Advanced pattern recognition.
- Context awareness.
- Smart substitution.
4. Address Substitution
- The malware compares against a whitelist (to avoid replacing its addresses).
- Selects an attacker-controlled address from its pool.
- Modifies the clipboard contents just before the paste operation.
- Optionally restores the original content after substitution to hide the attack.
5. C2 Communication and Updates
- Report successful hijacks and stolen amounts.
- Receive updated wallet addresses.
- Download new configuration or additional modules.
- Potentially uninstall itself after a set period.
6. Advanced Evasion Techniques
- Legitimate-looking process names.
- Traffic blends.
- Delayed activation.
- Code obfuscation.


