Invicta Stealer 2025
Cyber threats continue to evolve, with information-stealing malware playing a significant role in modern attacks. One such example is a powerful stealer that emerged in 2025, capable of extracting sensitive data from infected systems with alarming efficiency. Invicta Stealer 2025 stealers are often distributed through phishing campaigns, malicious downloads, or exploit kits, enabling attackers to harvest credentials, financial data, and other valuable information. Their modular design and evasion techniques make them a persistent threat to individuals and organizations alike, often serving as the first stage in more extensive cybercriminal operations.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
This type of malware is designed to collect and exfiltrate data from compromised systems covertly. It primarily targets login credentials, browser cookies, cryptocurrency wallets, and system information, which are then sent to a command-and-control (C2) server controlled by the attacker. Cybercriminals typically use the stolen data for identity theft, financial fraud, or resale on underground markets. The software is often bundled with other malicious tools or distributed as part of a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) model, making it accessible to less technically skilled threat actors.
Key Features of Invicta Stealer 2025
| Feature | Description |
| Credential Harvesting | Extracts saved passwords from browsers, email clients, and FTP applications. |
| Cookie Theft | Steals session cookies to bypass authentication and hijack accounts. |
| File Grabber | Searches for and exfiltrates specific file types (e.g., documents, logs). |
| System Profiling | Collects hardware, OS, and network details for targeted attacks. |
| Anti-Detection | Uses obfuscation, process hollowing, or sandbox evasion to avoid detection. |
| C2 Communication | Encrypts and sends stolen data to a remote server via HTTPS or custom protocols. |
| Persistence | Establishes auto-start mechanisms to remain active after system reboots. |
How Invicta Stealer 2025 Works
1. Infection and Execution
Invicta Stealer 2025 often infiltrates systems through deceptive methods like disguised email attachments, fake software updates, or compromised websites. Once a user activates the malicious file, the malware typically injects itself into legitimate processes using techniques such as process injection or DLL sideloading. This allows it to blend into system activity and reduce suspicion. In many cases, it disables security software by forcefully terminating related processes or tampering with Windows Defender settings.
2. Data Collection Techniques
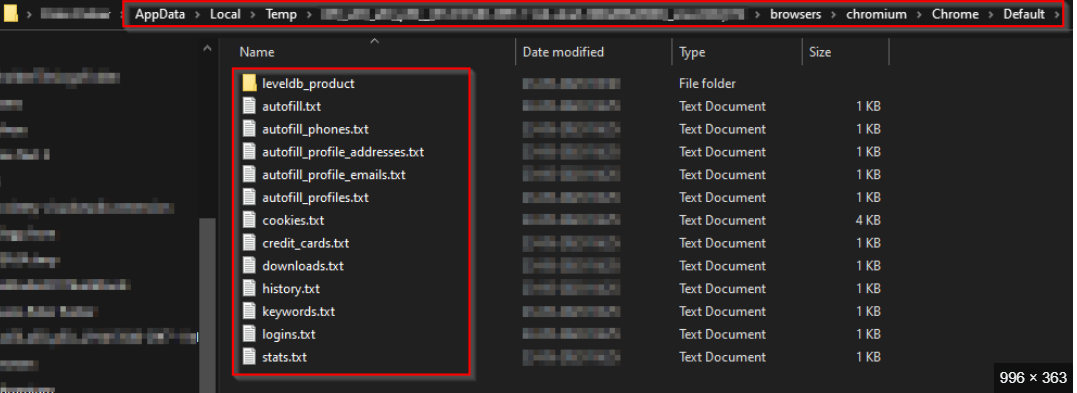
After establishing a presence on the system, Invicta Stealer aggressively scans for valuable data. It specifically targets:
Web Browsers: It extracts saved passwords, autofill entries, and cookies by directly querying browser databases.
Cryptocurrency Wallets: The malware searches for wallet files and pulls out private keys.
System Information: It gathers detailed data about installed software, hardware specs, and network settings to tailor follow-up attacks more effectively.
3. Evasion and Persistence
To stay undetected, Invicta Stealer employs several evasion strategies:
It uses code obfuscation to complicate reverse engineering and static analysis.
It checks for virtualized environments or sandbox tools before executing its main routines.
It maintains persistence by modifying system registries or leveraging scheduled tasks.
4. Payload Delivery and Data Exfiltration
Once it collects the data, Invicta Stealer compresses and encrypts it using algorithms like AES or XOR. It then transmits the stolen data to the attacker’s command-and-control (C2) server. To avoid detection, it often uses HTTPS or custom network protocols to mimic regular web traffic and evade monitoring tools.
Depending on the attacker’s intent, Invicta Stealer might also deliver additional threats, including ransomware or remote access trojans (RATs).


