Loki Stealer V5 Final Release
Cyber threats continue to evolve, with malicious actors leveraging advanced tools to bypass security measures and compromise systems. One such tool, often distributed through underground forums, is designed to steal sensitive information while evading detection. Loki Stealer V5 Final Software exemplifies the growing sophistication of modern cyberattacks, where stealth and functionality combine to target sensitive information, including credentials, financial data, and other critical data. Its modular design and ability to exploit common security weaknesses make it a persistent threat in the cybersecurity landscape.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
This software is a type of information-stealing malware, primarily used to extract data from infected systems. It targets web browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, and other applications storing valuable user information. Typically distributed via phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploit kits, it operates discreetly in the background, exfiltrating data to remote servers controlled by attackers. Cybercriminals often use it for financial fraud, identity theft, or selling harvested data on the dark web.
Key Features of Loki Stealer V5 Final
| Feature | Description |
| Credential Harvesting | Extracts saved login details from browsers and applications. |
| Cookie Theft | Steals session cookies to hijack authenticated sessions. |
| Form Grabbing | Captures input from web forms, including passwords and payment details. |
| Screen Capture | Takes screenshots of the victim’s desktop for additional reconnaissance. |
| Keylogging | Logs keystrokes to capture typed credentials and messages. |
| Anti-Detection | Uses obfuscation and evasion techniques to avoid antivirus detection. |
| Data Exfiltration | Sends stolen data to a command-and-control (C2) server via encrypted channels. |
How Loki Stealer V 5 Final Works
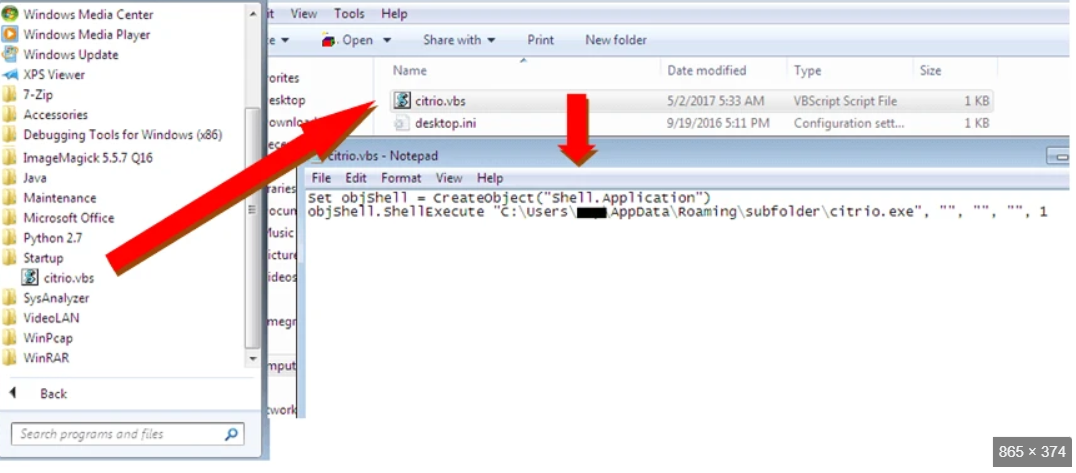
Infection and Execution
The malware typically infiltrates a system through social engineering, such as disguising itself as a legitimate file, or by exploiting software vulnerabilities. Once executed, it may employ process hollowing or DLL injection to run within a trusted process, reducing suspicion. Some variants also turn off security software or modify system settings to persist across reboots.
Data Collection Techniques
- Browser Targeting: The malware scans for browser profiles, extracting saved passwords, autofill data, and cookies. It decrypts stored credentials using built-in methods or by mimicking browser decryption routines.
- Wallet and Application Theft: It searches for installed cryptocurrency wallets or financial apps, copying private keys and configuration files.
- Keylogging and Form Grabbing: By hooking into system APIS, it records keystrokes and intercepts data entered into web forms before encryption.


