Mail Ripper 2024
Email remains one of the most exploited attack vectors in 2024, with cybercriminals constantly developing new tools to bypass security measures. Among these threats, specialized email cracking utilities have become particularly dangerous, enabling attackers to systematically compromise email accounts through brute-force and credential-stuffing techniques. Consequently, tools like Mail Ripper 2024 pose a significant threat to both individuals and organizations. This is because compromised email accounts often serve as gateways to more sophisticated attacks, including business email compromise (BEC), identity theft, and network infiltration.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
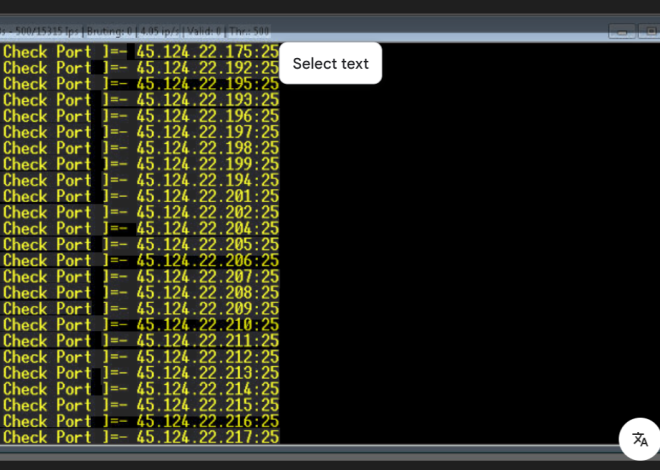
Specifically, this software is a high-performance email account cracking tool designed to test the validity of credentials across multiple email providers. To achieve this, it combines brute-force, dictionary, and credential-stuffing attacks into a single automated system. While security professionals might use similar tools for penetration testing, in contrast, malicious actors primarily deploy it to gain unauthorized access to email accounts. Moreover, the software supports attacks against major email services including Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, and corporate Exchange servers. Notably, it includes features specifically designed to evade modern security protections like CAPTCHA and two-factor authentication (2FA).
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Multi-Protocol Support | Works with POP3, IMAP, SMTP, and webmail interfaces |
| Proxy Chaining | Rotates through multiple proxy servers to avoid IP blocking |
| CAPTCHA Bypass | Integrates with solving services to overcome authentication challenges |
| 2FA Workarounds | Uses session hijacking techniques for accounts with two-factor auth |
| Adaptive Throttling | Automatically adjusts attack speed based on server responses |
| Pattern Recognition | Identifies common password formats (dates, phrases, character substitution) |
| Distributed Attack Mode | Spreads workload across multiple machines for increased speed |
How Mail Ripper 2024 Works
1. Target Acquisition and Preparation
To begin with, the attacker loads a list of target email addresses, which are often obtained from data breaches or phishing campaigns. Next, password lists are compiled using credentials from previous leaks or generated based on common patterns. After that, the attacker configures various parameters, including protocol selection (IMAP, SMTP, or webmail), timeout settings, and success criteria.
2. Attack Execution
Credential Testing Phase:
Once the preparation is complete, the tool systematically attempts logins using the supplied credentials. In the case of webmail services, it mimics legitimate browser behavior by injecting proper headers and managing cookies. Furthermore, it captures session tokens when possible, which helps bypass subsequent authentication steps.
Evasion Techniques:
To avoid detection, the tool distributes traffic across multiple proxy endpoints, thereby reducing the risk of IP-based blocking. Additionally, it randomizes request timing to simulate human-like login behavior. As a result, the tool can operate under the radar of many security systems.
3. Response Analysis
Following the attack phase, the tool analyzes server responses to determine which logins were successful. It verifies access by checking inbox contents or by identifying specific server messages. Moreover, it flags partial successes—such as valid usernames with incorrect passwords—for more targeted future attempts.
4. Post-Compromise Actions
After gaining access, Mail Ripper 2024 enables attackers to carry out a series of malicious actions:
Export contact lists to facilitate further phishing or spam campaigns
Set up mail forwarding rules to maintain long-term access
Search mailboxes for sensitive information, such as financial data or stored credentials
Plant persistent access methods through malicious filters or email signatures
Ultimately, these capabilities make the tool extremely dangerous, especially in the hands of less-experienced attackers who rely on automation to breach and exploit email systems.