Multi VPN Checker 2025
In 2025, multi-VPN checkers have become a double-edged sword in cybersecurity. While legitimate users rely on them to verify VPN functionality and privacy, threat actors increasingly exploit these tools to conduct sophisticated cyberattacks. By testing multiple VPN connections, attackers can identify weak points, evade geo-restrictions, and mask their malicious activities. Multi VPN Checker 2025 makes multi-VPN checkers a valuable asset in bypassing security measures, enabling attacks such as credential stuffing, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS), and data exfiltration while remaining undetected.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
This software is designed to assess and validate multiple VPN connections simultaneously, ensuring optimal performance, anonymity, and reliability. Typically, it is used by cybersecurity professionals, penetration testers, and privacy-conscious individuals to verify VPN integrity. However, malicious actors repurpose it to test stolen credentials, rotate IP addresses, and distribute payloads across different VPN endpoints, making attribution difficult.

Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Multi-VPN Testing | Simultaneously checks multiple VPN connections for stability and speed. |
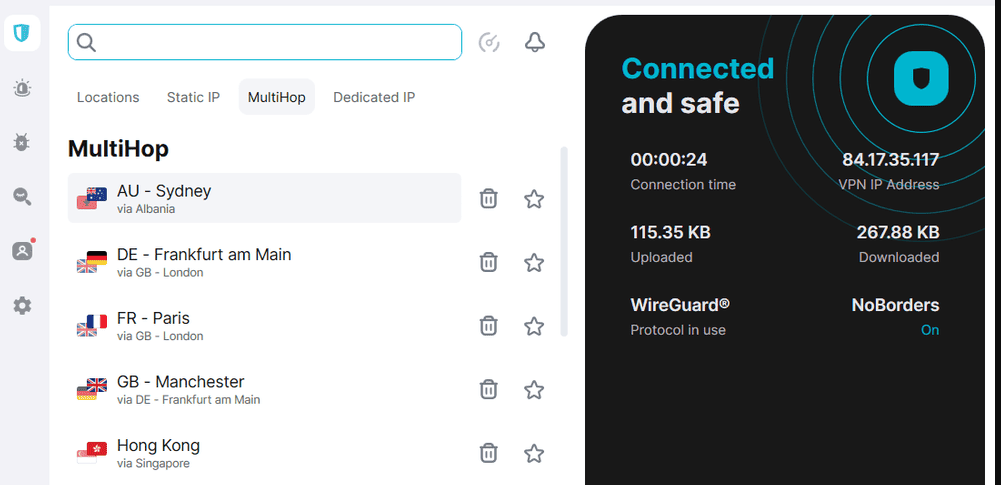
| IP Rotation | Automatically switches between VPN servers to avoid detection. |
| Geo-Spoofing | Tests VPNs against different geographic restrictions. |
| Logging & Reporting | Records connection logs for analysis, which can be abused for reconnaissance. |
| Anonymity Validation | Verifies if DNS/IP leaks exist, ensuring true anonymity. |
| Custom Payload Delivery | Allows integration with malicious scripts for targeted attacks. |
How Multi VPN Checker 2025 Works
The software operates by establishing connections to multiple VPN servers, either through pre-configured profiles or dynamically acquired credentials. It employs the following techniques:
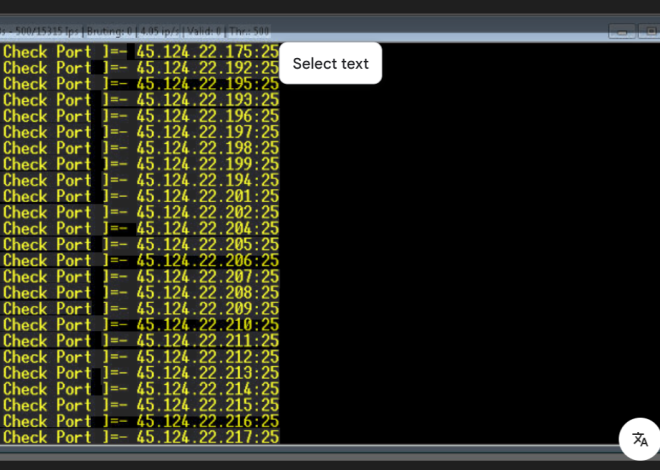
- Connection Testing – The tool pings each VPN server, measures latency, and checks for DNS/IP leaks to ensure the connection is secure and anonymous. Attackers use this to confirm their traffic is untraceable before launching attacks.
- IP Rotation & Load Balancing – By cycling through different VPN endpoints, the software distributes traffic across multiple exit nodes. This technique helps evade rate-limiting and blacklisting mechanisms employed by target systems.
- Payload Delivery – If weaponized, the software can inject malicious payloads (e.g., malware, phishing links) through the VPN tunnels. Since each payload originates from a different IP, security systems struggle to correlate the attacks.
- Geo-Spoofing & Bypassing Restrictions – The tool verifies whether a VPN can bypass geo-blocks, which attackers exploit to access restricted systems or conduct region-specific attacks.
- Logging & Reconnaissance – Connection logs are stored, detailing successful and failed VPN connections. Threat actors analyze these logs to identify vulnerable VPN providers or misconfigured servers for future exploitation.
By leveraging these functionalities, the software ensures seamless VPN switching while providing attackers with a robust infrastructure for stealthy cyber operations. Its legitimate use cases are overshadowed by its potential for abuse, making it a critical tool in modern cyberattack frameworks.