Phoenix Keylogger 2025
Phoenix Keylogger 2025 has emerged as one of the most advanced and stealthy keylogging tools in the cybercriminal arsenal, representing a significant leap in credential theft and surveillance capabilities. This latest iteration of the notorious malware has been observed in high-profile attacks against corporate networks, financial institutions, and individual users, demonstrating alarming improvements in evasion techniques and data exfiltration. Security researchers have documented its use in business email compromise (BEC) schemes, banking fraud, and corporate espionage, where attackers leverage its ability to bypass modern endpoint detection systems. The 2025 version introduces AI-assisted behavioral analysis, allowing it to selectively log high-value keystrokes while avoiding detection by blending in with normal system activity.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4

What is the Phoenix Keylogger
This software is a sophisticated keystroke-logging tool designed to capture and exfiltrate sensitive input from infected systems, including passwords, credit card details, and private communications. Unlike basic keyloggers, Phoenix Keylogger 2025 operates at both the kernel and user levels, making it exceptionally difficult to detect and remove. Cybercriminals typically deploy it through:
- Phishing emails.
- Trojanized software.
- Drive-by downloads.
- Malicious browser extensions.
Once installed, it enables attackers to:
- Capture keystrokes.
- Record clipboard data.
- Take periodic screenshots.
- Log form submissions.
- Exfiltrate credentials.
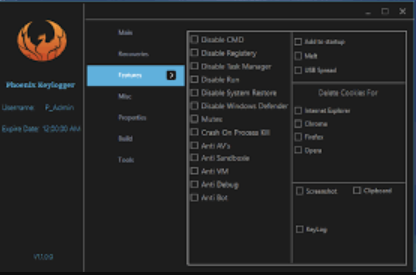
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| AI-Powered Keystroke Filtering | Prioritizes high-value inputs (logins, credit cards) while ignoring noise |
| Kernel-Level Operation | Runs at a low system level to evade user-mode security scans |
| Clipboard Monitoring | Captures copied text, including crypto transactions and sensitive data |
| Form Grabbing | Intercepts web form submissions before encryption |
| Screenshot Capture | Takes images of active windows during login attempts or sensitive actions |
| Encrypted Exfiltration | Sends stolen data via HTTPS, Telegram, or FTP in encrypted logs |
| Persistence Mechanisms | Survives reboots via registry modifications, scheduled tasks, or rootkits |
| Anti-Sandboxing | Detects virtual environments and delays execution to avoid analysis |
How the Phoenix Keylogger works
1. Delivery and Initial Infection
The keylogger spreads through multiple vectors:
- Spear phishing with socially engineered lures (e.g., fake invoices, HR documents).
- Exploit kits target unpatched software vulnerabilities.
- Malicious ads redirecting to payload-dropping sites.
Upon execution, it:
- Drops payloads in hidden directories (%AppData%, %Temp%).
- Injects into legitimate processes (e.g., explorer.exe, svchost.exe).
- Disables security features (Windows Defender, firewalls) via PowerShell commands.
- Establishes persistence through registry run keys or WMI event subscriptions.
2. Data Capture Techniques
The malware employs multiple methods to harvest sensitive input:
Keystroke Logging:
- Hooks keyboard APIs at the kernel level.
- Logs keystrokes even in secure input fields (e.g., banking portals).
- Uses AI to identify high-value sessions (login pages, payment forms).
Clipboard Hijacking:
- Monitors for cryptocurrency addresses, passwords, or confidential text.
- Captures data before it’s pasted into applications.
Form Grabbing:
- Intercepts web form submissions before HTTPS encryption.
- Targets login pages, checkout flows, and authentication dialogs.
Screenshot Capture:
- Triggers screenshots when detecting password fields or banking sites.
- Uses OCR to extract text from images.
3. Data Exfiltration and C2 Communication
Stolen data is:
- Compressed and encrypted locally
- Transmitted via multiple channels:
- HTTPS.
- Telegram bots.
- Cloud storage.
- Structured in logs.
4. Evasion and Anti-Forensics
To avoid detection, the keylogger uses:
- Process hollowing.
- Code obfuscation.
- Dynamic API resolution.
- User-mode rootkit.
- Delayed activation.


