Proton Crypter V 2.0
In the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, Proton Crypter V 2.0 has emerged as a critical tool for attackers who aim to evade detection and deploy malicious payloads. These programs are specifically designed to obfuscate and encrypt harmful code, thereby making it extremely difficult for traditional antivirus solutions to identify and block them.
Consequently, modern cyberattacks—such as ransomware, spyware, and trojans—frequently rely on crypters to bypass security measures. By doing so, attackers can infiltrate systems undetected, often remaining hidden for extended periods. As a result, cybersecurity professionals face an ongoing battle: as detection techniques become more advanced, so too do the capabilities of crypters. Therefore, these tools continue to pose a persistent and evolving threat.
This software is, in essence, a crypter—a specialized tool used to encrypt and obfuscate malicious executables. In doing so, it renders them undetectable by signature-based antivirus programs. Typically, threat actors employ it to help malware bypass traditional security defenses by disguising the payload as legitimate code.
Furthermore, the primary use cases include delivering ransomware, remote access trojans (RATs), and keyloggers. Nevertheless, Proton Crypter V 2.0 is not exclusively used for malicious purposes. In fact, it can also be repurposed for ethical penetration testing within controlled environments, allowing security teams to test and strengthen their own defenses.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
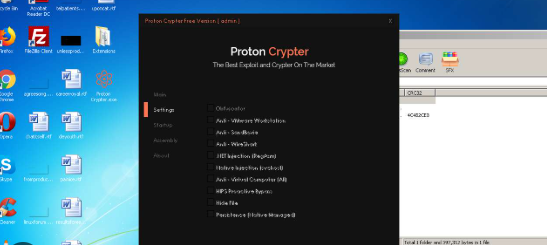
Key Features of Proton Crypter V 2.0
| Feature | Description |
| Advanced Encryption | Uses strong cryptographic algorithms to mask malicious code. |
| AV Evasion | Bypasses heuristic and signature-based detection. |
| Payload Injection | Injects encrypted payloads into legitimate processes. |
| Polymorphic Code | Dynamically alters code structure to avoid static analysis. |
| Process Hollowing | Replaces a benign process’s memory with malicious code. |
| Customizable Stub | Allows attackers to generate unique decryption routines for each payload. |
How Proton Crypter V 2.0 Works
Below is a breakdown of its functionality:
- Payload Encryption – The original malicious executable is encrypted using an algorithm (e.g., AES or RSA).
- Stub Generation – The stub contains a decryption routine that unpacks and executes the payload in memory. Polymorphic techniques may alter the stub’s code structure to avoid signature detection.
- Execution and Injection – Upon running the stub, it decrypts the payload and injects it into a legitimate system process (e.g., explorer.exe or svchost.exe) using techniques such as process hollowing or DLL Injection. This step helps evade behavioural analysis.
- Persistence Mechanisms – Depending on configuration, the payload may establish persistence via registry modifications, scheduled tasks, or service installations.
By leveraging these techniques, the crypter ensures that the malicious payload remains undetected until it is successfully deployed within the target system. The use of encryption, code obfuscation, and process injection makes it a formidable tool in the hands of attackers, emphasizing the need for advanced behavioural detection methods in cybersecurity defences.