ToxicEye RAT STEALER CLIPPER 2025
Modern cyberattacks increasingly leverage multi-functional malware that combines multiple malicious capabilities into a single, potent threat. Among these, hybrid malware that blends remote access functionality with data theft and financial fraud features has become particularly dangerous. The 2025 version of ToxicEye RAT STEALER CLIPPER demonstrates how cybercriminals are evolving their tools to maximize impact, combining credential theft, remote control, and cryptocurrency fraud into one sophisticated package. These Swiss Army knife-style threats pose significant challenges to defenders as they can adapt their attack methods based on what they find on infected systems.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
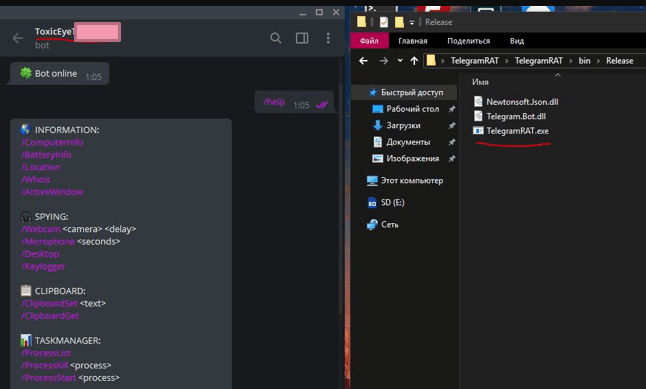
This malware represents a dangerous evolution in cybercriminal tools, combining three major malicious functions into a single payload. It operates as a remote access trojan, information stealer, and clipboard hijacker simultaneously. Distributed primarily through phishing campaigns and malicious downloads, it first establishes persistence on a victim’s machine before beginning its multifaceted attack. Cybercriminals value this type of malware for its versatility – it can be used to steal sensitive data, take control of systems, and divert cryptocurrency payments, all while maintaining a low profile to avoid detection.

Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Remote Access Trojan | Provides full system control through hidden VNC and command shell |
| Credential Stealer | Harvests passwords, cookies, and tokens from browsers and applications |
| Clipboard Hijacker | Monitors and replaces cryptocurrency wallet addresses in the clipboard |
| Process Injection | Executes malicious code within legitimate processes to evade detection |
| Screen Capture | Periodically captures screenshots of user activity |
| Keylogging | Records all keystrokes, including sensitive inputs |
| Persistence Mechanisms | Maintains access through registry modifications and scheduled tasks |
| Encrypted C2 | Uses strong encryption for all command and control communications |
| Anti-Analysis | Detects and avoids sandboxes, virtual machines, and debugging environments |
How ToxicEye RAT STEALER CLIPPER Works
Infection and Initial Compromise
The malware typically enters systems through:
- Spear Phishing Emails: Messages with malicious Office documents or PDF attachments
- Fake Software Updates: Compromised websites offering fraudulent updates for common applications
- Social Engineering: Download links disguised as game mods or productivity tools
The infection process follows several stages:
- Initial Dropper: A seemingly harmless file executes and unpacks the malicious payload
- Environment Checks: Verifies it’s not running in analysis environments
- Persistence Setup: Installs itself using multiple methods, including:
- Registry Run keys
- Scheduled tasks
- Windows service creation
Core Malicious Functionality
Once established, the malware activates its three primary attack vectors:
- Remote Access Capabilities
- Establishes hidden VNC sessions undetectable to the user
- Provides full file system access for data exfiltration
- Enables remote command execution through PowerShell and CMD
- Information Stealing Operations
- Targets browser data (Chrome, Firefox, Edge) for saved credentials
- Extracts authentication tokens from email clients and messaging apps
- Scans documents and databases for sensitive information
- Captures screenshots during login activities
Cryptocurrency Hijacking
- Monitors the clipboard for cryptocurrency wallet patterns
- Maintains a database of attacker-controlled addresses
- Implements smart replacement that considers:
- Transaction context
- Amount being transferred
- Wallet type (BTC, ETH, etc.)
Evasion and Anti-Detection Techniques
The malware employs advanced methods to avoid discovery:
- Code Obfuscation: Uses polymorphic techniques to change its signature
- Living-off-the-Land: Leverages legitimate system tools for malicious purposes
- Network Camouflage: Blends C2 traffic with normal web activity
- Delayed Activation: Waits until the system is active before beginning operations
Command and Control Infrastructure
Communication with attacker servers occurs through:
- HTTPS Channels: Encrypted traffic blending with normal web activity
- Decentralized Systems: Some versions use blockchain or peer-to-peer networks
Dead Drop Resolving: Retrieves C2 information from public platforms like GitHub or Pastebin


