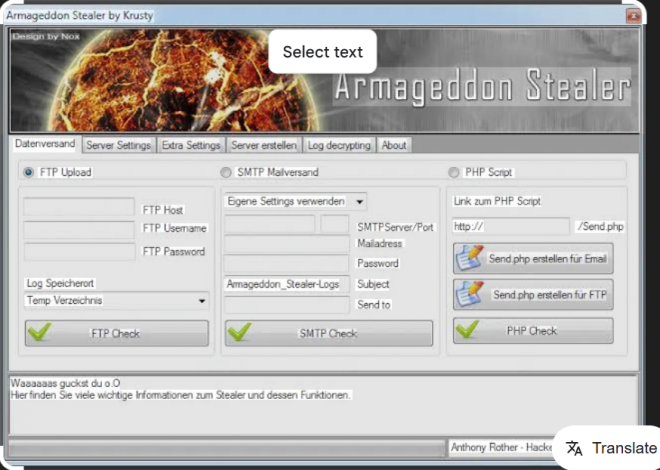
Ultimate Hacking Pack 2024
The Ultimate Hacking Pack 2024 is a comprehensive toolkit designed for penetration testing and vulnerability assessment, capable of scanning networks, web applications, and systems for security weaknesses. Initially developed for ethical hacking and security research, this toolkit has, unfortunately, been increasingly weaponized in modern cyberattacks. Threat actors now leverage their capabilities to conduct reconnaissance, exploit vulnerabilities, and deploy malicious payloads, making it a dual-use tool that poses significant risks in the wrong hands.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Ultimate Hacking Pack 2024 software bundles a wide array of offensive security tools and scripts into a single package. While cybersecurity professionals and red teams use it to simulate attacks and strengthen defenses, malicious actors abuse its functionalities to automate attacks, bypass security measures, and maintain persistence in compromised systems. Common use cases include network penetration testing, password cracking, and post-exploitation activities, but its modular design also allows for extensive customization in adversarial operations.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Scanning | Identifies live hosts, open ports, and running services. |
| Vulnerability Assessment | Detects known vulnerabilities in software and configurations. |
| Exploitation Framework | Provides pre-built exploits for common vulnerabilities. |
| Password Cracking | Supports brute-force and dictionary attacks against weak credentials. |
| Post-Exploitation Tools | Enables lateral movement, privilege escalation, and data exfiltration. |
| Web Application Testing | Scans for SQLi, XSS, and other web-based flaws. |
| Custom Scripting | Allows users to modify or create new attack modules. |
How It Works
The software operates through a multi-stage process, combining automated scanning, exploitation, and post-exploitation techniques. Below is a detailed breakdown of its functionality:
1. Reconnaissance & Scanning
The toolkit first performs ICMP ping sweeps, TCP/UDP port scanning, and service fingerprinting to gather intelligence about target systems. Afterward, it analyzes response patterns to identify potential entry points while cataloging system characteristics for further exploitation.
In the case of web applications, it methodically crawls through all accessible pages and inputs. Following this initial mapping phase, it systematically tests each element for vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection (SQLi) and cross-site scripting (XSS). Throughout this process, it continuously maps the application’s attack surface, building a complete vulnerability profile.
2. Vulnerability Exploitation
Once vulnerabilities are identified, the toolkit leverages its built-in exploit modules to deliver payloads. These exploits may target unpatched software, weak configurations, or misapplied permissions. Depending on the attack, payloads can range from simple command execution to advanced memory corruption exploits or remote code execution (RCE).
3. Payload Delivery & Execution
Payloads are typically delivered through:
Crafted network packets
Malicious web requests
Social engineering (e.g., phishing emails with embedded exploits)
To evade detection, the toolkit often employs obfuscation, encryption, or traffic fragmentation.
4. Post-Exploitation Activities
After gaining initial access, the software provides tools for:
Privilege escalation (e.g., dumping credentials)
Lateral movement (spreading across the network)
Persistence mechanisms (e.g., backdoors, scheduled tasks, rootkits)
- Data exfiltration (stealing sensitive information)
5. Evasion Techniques
To avoid detection, the toolkit can:
Fragment network traffic
Use encrypted channels (e.g., HTTPS, DNS tunneling)
Mimic legitimate traffic patterns