WarZone RAT 3.03 Cracked
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, Remote Access Trojans (RATs) continue to be a weapon of choice for malicious actors seeking unauthorized access to sensitive systems. The availability of cracked versions of commercial RATs on underground forums has significantly lowered the barrier to entry, enabling even low-skilled attackers to deploy sophisticated surveillance and data theft operations. These tools are frequently employed in financial fraud, corporate espionage, and large-scale data breaches, posing serious risks to individuals and organizations worldwide. The stealthy nature of WarZone RAT 3.03 combined with their extensive functionality, makes them particularly challenging to detect and mitigate.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
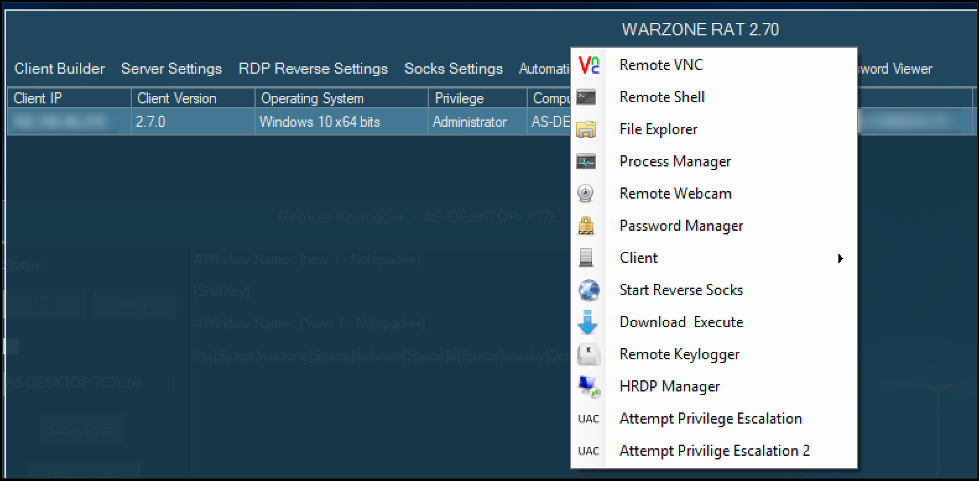
This software is a powerful, commercially developed Remote Access Trojan that has been repackaged and distributed illegally in cracked form. It provides attackers with complete control over compromised systems, enabling them to steal sensitive information, monitor user activity, and execute malicious commands remotely. Typically distributed through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploit kits, this RAT is often used to harvest banking credentials, capture keystrokes, and exfiltrate valuable data. Its modular design allows for additional functionality to be loaded post-infection, making it a versatile tool for cybercriminals engaged in both targeted attacks and widespread campaigns.

Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Remote System Control | Full access to file system, processes, and command execution capabilities. |
| Keylogging | Records all keystrokes to capture passwords and other sensitive input. |
| Screen Capture | Takes screenshots or records the victim’s desktop in real time. |
| Webcam & Mic Access | Enables covert audio/video surveillance through connected devices. |
| Data Exfiltration | Searches for and steals documents, credentials, and cryptocurrency wallets. |
| Persistence | Maintains access through registry modifications and hidden startup entries. |
| Anti-Detection | Uses code obfuscation, process injection, and VM/sandbox evasion techniques. |
How WarZone RAT 3.03 Works
Infection and Initial Execution
The malware typically gains access to systems through:
- Phishing Campaigns: Emails with malicious attachments (e.g., fake invoices, resumes) that execute the payload
- Drive-by Downloads: Compromised websites that exploit browser vulnerabilities to install the RAT silently
- Social Engineering: Fake software cracks or pirated applications that bundle the malicious payload
Once executed, it establishes persistence through:
- Registry modifications (e.g., HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run)
- Creation of scheduled tasks for periodic reactivation
- Disabling security tools via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) commands
Core Functionality
After successful installation, the RAT performs multiple malicious activities:
- System Reconnaissance
- Gathers detailed system information (OS version, installed software, hardware specs)
- Identifies security software running on the victim machine
- Data Harvesting
- Logs keystrokes to capture credentials and sensitive communications
- Dumps saved passwords from browsers and email clients
- Scans for cryptocurrency wallet files and sensitive documents
- Surveillance Capabilities
- Activates webcam and microphone for covert monitoring
- Captures screenshots at regular intervals or triggered by specific events
- Remote Control
- Provides shell access for executing arbitrary commands
- Enables file upload/download functionality
- Allows attackers to manipulate the system in real-time
Evasion and Communication Techniques
The RAT employs several advanced methods to avoid detection:
- Process Hollowing: Injects malicious code into legitimate processes (e.g., svchost.exe)
- Encrypted C2 Traffic: Uses HTTPS or custom encryption for command and control communications
- Domain Generation Algorithms (DGA): Dynamically generates C2 domains to bypass blocklists
- Delayed Execution: Waits for specific conditions (e.g., idle time) before activating
Data exfiltration typically occurs through:
- Encrypted connections to attacker-controlled servers
- Cloud storage services as intermediate drop points
- Peer-to-peer networks for decentralized C2 infrastructure


