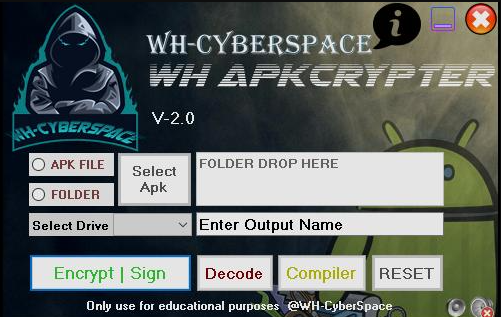
WH ApkCrypter V2
In the evolving landscape of cybersecurity, malicious actors increasingly rely on advanced tools to bypass detection and deploy harmful payloads. One such tool, known for its ability to evade traditional security measures, is the WH ApkCrypter V2. This type of software plays a significant role in modern cyberattacks, particularly in obfuscating malware to avoid analysis by antivirus programs and security researchers. By encrypting or modifying malicious code, these tools enable attackers to distribute harmful applications while remaining undetected, posing a serious challenge to mobile and endpoint security.
This software is a specialised crypter designed to modify and obfuscate Android application packages (APKS). Typically used by threat actors, its primary purpose is to encrypt or transform malicious APK files, making them appear benign to security scanners. The tool is often employed in phishing campaigns, spyware distribution, and ransomware attacks, where avoiding detection is critical. By modifying the code structure and implementing encryption layers, the software enables malware to evade signature-based detection while preserving its original functionality.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Code Obfuscation | Scrambles the APK’s code to hinder reverse engineering and analysis. |
| Encryption Layers | Applies multiple encryption methods to hide malicious payloads. |
| Anti-Debugging Tricks | Detects and prevents dynamic analysis in sandboxed environments. |
| Signature Spoofing | Mimics legitimate app signatures to bypass integrity checks. |
| Payload Injection | Embeds additional malicious code into seemingly harmless applications. |
| Compression Techniques | Reduces file size while maintaining obfuscation to avoid detection. |
How WH ApkCrypter Works
The software operates by taking an input APK (often containing malware) and processing it through several stages to evade detection. Below is a breakdown of its functionality:
- Code Transformation
The tool first disassembles the original APK, restructuring its code using obfuscation techniques such as renaming variables, inserting junk code, or altering control flow. This makes static analysis difficult for security tools. - Encryption
The malicious payload is encrypted using algorithms (e.g., AES or custom ciphers), with decryption routines embedded within the APK. When the app runs, the payload is decrypted in memory, avoiding detection by file-based scanners. - Anti-Analysis Measures
To prevent security researchers from examining the APK, the software may include checks for emulators, debuggers, or sandbox environments. If detected, the malware may terminate or delay execution. - Payload Delivery
Once the app is installed and executed, the decrypted payload is deployed. This could involve downloading additional malware, stealing data, or establishing a connection to a command-and-control (C2) server. - Persistence Mechanisms
Some variants ensure long-term access by exploiting Android permissions, hiding app icons, or registering background services that restart after device reboots.
By combining these techniques, the software effectively disguises malicious activity, making it a potent tool for cybercriminals targeting mobile and connected systems. Security professionals must rely on behavioral analysis and advanced threat detection methods to identify such threats.