WiFi Hacking for Beginners 2025
WiFi hacking remains a critical concern in modern cybersecurity, as wireless networks are often the weakest link in an organization’s defense. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in WiFi Hacking for Beginners 2025, weak encryption, or poor configuration to gain unauthorized access, intercept data, or deploy malware. In 2025, beginner-friendly tools have made these attacks more accessible, allowing even novice hackers to execute sophisticated intrusions with minimal technical expertise. Understanding how these tools operate is essential for cybersecurity professionals to defend against such threats.
What Is WiFi Hacking?
WiFi hacking software is a penetration testing tool designed to assess and exploit weaknesses in WiFi networks. While its primary purpose is for ethical hacking and security research, it is frequently misused for malicious activities. The tool automates attacks such as deauthentication, handshake capture, and brute-force decryption, enabling attackers to crack passwords, eavesdrop on traffic, or gain network access. Its user-friendly interface and pre-configured attack modules make it particularly appealing to beginners.
Key Features of WiFi Hacking
| Feature | Description |
| Deauthentication Attacks | Forces devices to disconnect from a network, capturing authentication handshakes. |
| WPA/WPA2 Cracking | Uses dictionary or brute-force attacks to decrypt captured handshake files. |
| Rogue Access Point | Creates fake WiFi networks to trick users into connecting. |
| Packet Sniffing | Intercepts and analyzes unencrypted network traffic. |
| Automated Attack Sequences | Executes multi-stage attacks with minimal manual input. |
| GUI & CLI Support | Offers both graphical and command-line interfaces for flexibility. |
How the WiFi Hacking Works
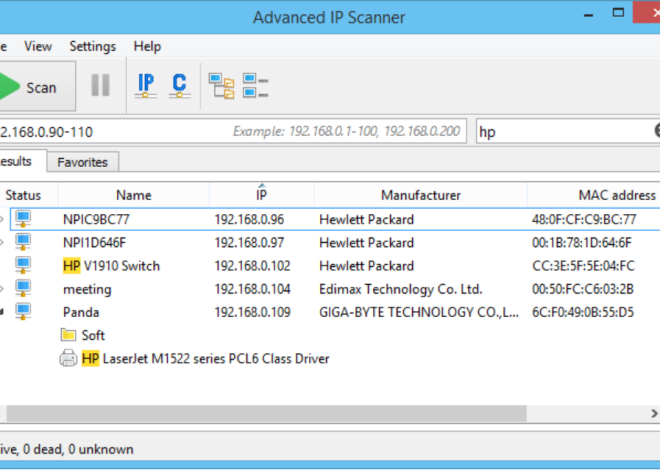
Network Discovery & Reconnaissance
The tool scans for nearby WiFi networks using standard wireless adapters in monitor mode. It identifies targets by analyzing SSIDs, signal strength, and encryption types (e.g., WEP, WPA2, WPA3).
Deauthentication Attacks
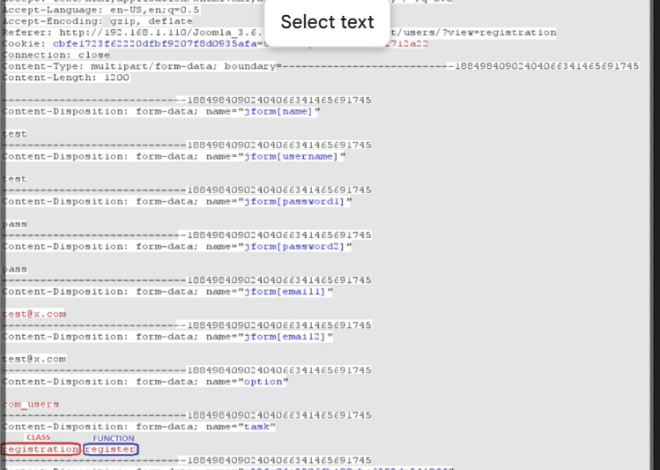
By sending forged deauthentication packets, the tool disconnects devices from a target network. This forces devices to reconnect, allowing the capture of the WPA/WPA2 four-way handshake—a crucial step for offline password cracking.
Handshake Capture & Cracking
Once a handshake is captured, the software uses preloaded wordlists or brute-force techniques to guess the password. Advanced versions leverage GPU acceleration for faster decryption.
Rogue Access Point (Evil Twin)
The tool clones a legitimate network’s SSID, tricking users into connecting to it. Attackers can then intercept traffic, inject malware, or steal credentials via phishing pages.
Packet Sniffing & MITM Attacks
If the network uses weak or no encryption, the software captures unencrypted data, such as HTTP traffic and login credentials. Some variants incorporate Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) modules to manipulate traffic in real-time.