x2 2021 Emv Writer
In recent years, advanced malware-writing tools have emerged as a significant threat to the cybersecurity landscape. Among these, x2 2021 Emv Writer has gained notoriety for its role in facilitating sophisticated cyberattacks, particularly in financial fraud and data theft. These tools empower attackers to create and deploy malicious payloads with relative ease, often bypassing traditional security measures. Their modular design and evasion techniques make them a persistent challenge for defenders, primarily when used in targeted attacks against payment systems and sensitive databases.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
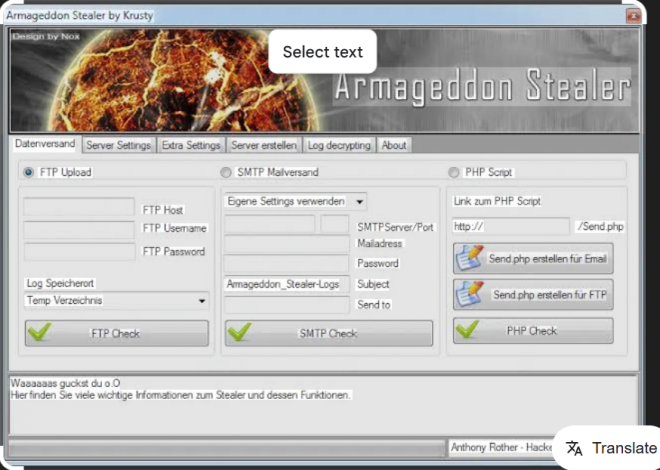
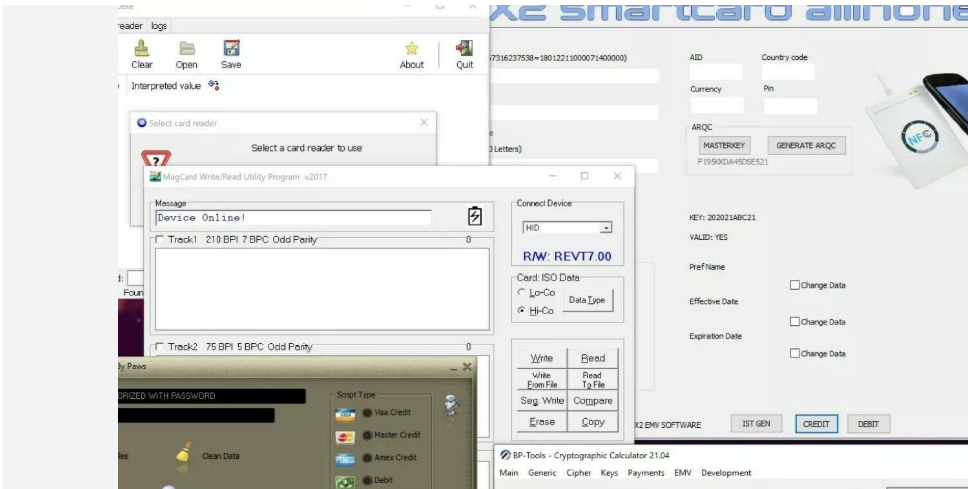
x2 2021 Emv Writer is a specialized tool designed to generate and manipulate malicious scripts, primarily targeting payment card systems and embedded devices. It is often used in attacks involving EMV (Europay, Mastercard, Visa) chip-enabled cards, where it can facilitate unauthorized transactions or data extraction. The software is typically distributed through underground forums and is favored by cybercriminals for its ability to automate the creation of fraudulent card data. While it has legitimate applications in security research, its misuse in financial fraud has made it a key concern for law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals.
Key Features of x2 2021 EMV Writer
| Feature | Description |
| EMV Data Manipulation | Modifies EMV chip data to bypass transaction security checks. |
| Payload Generation | Creates executable scripts tailored for specific card reader vulnerabilities. |
| Stealth Mechanisms | Uses obfuscation and encryption to evade detection by antivirus software. |
| Automated Fraud Scripts | Generates pre-configured attack sequences for rapid deployment. |
| Multi-Platform Support | Compatible with various card reader models and operating systems. |
How the Software Works
The tool operates through a combination of data manipulation, script injection, and evasion techniques to execute its payloads. Below is a breakdown of its functionality:
Data Extraction & Manipulation
The software first interfaces with a compromised card reader or a cloned EMV chip, extracting encrypted card data. It then decrypts and modifies critical fields (e.g., transaction counters, PIN verification values) to bypass security checks.
Payload Generation
Using predefined templates, the tool generates malicious scripts tailored to the target system. These scripts may include:
- Transaction Overrides – Forcibly approve unauthorized payments.
- Data Skimming Modules – Logs and exfiltrate cardholder details.
Evasion Techniques
To avoid detection, the software employs:
- Code Obfuscation – Scrambles script logic to hinder analysis.
- Dynamic Payloads – Alter malicious code in real-time to evade signature-based detection.
Payload Delivery
The final payload is delivered via:
- Physical Access – Directly installed on a compromised card reader.
- Remote Exploitation – Deployed through phishing or vulnerable POS (Point-of-Sale) systems.
Once executed, the malware either intercepts live transactions or clones card data for later use. Its modular design allows attackers to update attack vectors as security measures evolve, making it a persistent threat in financial cybercrime.