XWorm V3.1 Cracked
The cybersecurity landscape faces constant evolution as malware developers refine their tools to bypass modern defenses. Among these threats, XWorm V3.1 has emerged as a particularly dangerous remote access trojan (RAT) circulating in underground forums. This cracked version of sophisticated malware has lowered the barrier to entry for cybercriminals, enabling even novice attackers to deploy powerful surveillance and control capabilities. Unlike simpler malware variants, this threat combines multiple attack vectors into a single package, allowing comprehensive system compromise while evading traditional security solutions. Its availability in cracked form has led to widespread abuse in credential theft, ransomware deployment, and corporate espionage campaigns, making it a significant concern for both individual users and enterprise security teams.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
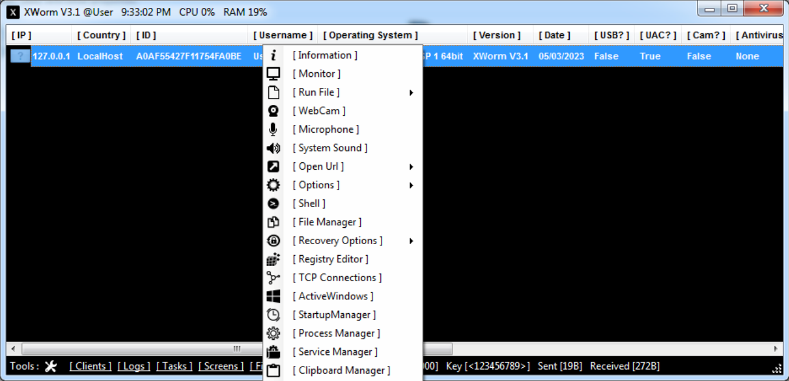
This software is a multi-featured remote administration tool repurposed for malicious activities. Functioning as a full-featured RAT, it provides attackers with complete control over compromised systems while incorporating additional modules for data theft and system exploitation. The cracked version removes licensing restrictions, making it freely available to cybercriminals while maintaining nearly all the capabilities of the original commercial version. Typical uses include corporate network infiltration, credential harvesting, cryptocurrency theft, and as a delivery mechanism for secondary payloads like ransomware or spyware. The malware is particularly notable for its modular architecture, allowing attackers to enable or disable features based on their specific objectives and target environment.

Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Remote Desktop Control | Full GUI access to victim machines |
| Credential Harvesting | Extracts passwords from browsers and email clients |
| Keylogging | Captures all keyboard input with application context |
| File Management | Upload/download/execute files on victim systems |
| Process Injection | Conceals malicious activity within legitimate processes |
| Persistence | Survives reboots via multiple mechanisms |
| Cryptocurrency Theft | Targets wallet files and clipboard contents |
| Network Propagation | Spreads laterally across connected networks |
| Anti-Analysis | Detects and evades virtual machines and sandboxes |
How XWorm V3.1 Works
1. Distribution and Infection
The malware employs multiple sophisticated delivery methods:
- Phishing Campaigns: Malicious email attachments disguised as invoices or documents
- Software Cracks: Bundled with pirated versions of popular applications
- Fake Updates: Compromised websites offering fraudulent software patches
- Malvertising: Malicious advertisements redirecting to exploit kits
2. Initial Execution and Installation
Upon successful delivery:
- Environmental Checks:
- Detects virtual machines, sandboxes, and analysis tools
- Identifies security software and potential monitoring solutions
- Persistence Mechanisms:
- Creates registry entries in multiple locations
- Installs as a Windows service with deceptive name
- Establishes scheduled tasks for regular reactivation
- Process Injection:
- Injects malicious code into explorer.exe or other trusted processes
- Uses reflective DLL injection to avoid disk writes
3. Core Malicious Functionality
Once established, the malware activates multiple attack modules:
Remote Access Capabilities
- Establishes reverse shell connections to C2 servers
- Provides real-time desktop viewing and control
- Enables remote webcam and microphone activation
- Offers file system navigation and manipulation
Data Harvesting Operations
- Extracts saved credentials from:
- Web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge)
- Email clients (Outlook, Thunderbird)
- FTP clients and VPN software
- Collects cryptocurrency wallet files and clipboard contents
- Captures screenshots at configurable intervals
Network Propagation
- Scans local networks for vulnerable systems
- Attempts lateral movement using:
- Exploits for EternalBlue and similar vulnerabilities
- Brute force attacks on weakly secured RDP connections
- Stolen credential reuse across systems
4. Command and Control Communication
The malware employs sophisticated C2 infrastructure:
- Primary Channels:
- Encrypted HTTPS connections mimicking legitimate traffic
- Domain generation algorithms (DGA) for resilient C2 access
- Fallback Mechanisms:
- Decentralized communication through peer-to-peer networks
- Blockchain-based commands via smart contracts
- Data Exfiltration:
- Compresses and encrypts stolen data before transmission
- Uses steganography techniques to hide data in image files
5. Advanced Evasion Techniques
To maintain persistence and avoid detection:
- Code Obfuscation: Regularly morphs binary signatures
- Traffic Mimicry: Blends with legitimate cloud service traffic
- User Behavior Analysis: Remains dormant during active user sessions
- Competitive Process Termination: Disables competing malware


