Zeroday Link exploit 2024
Zero-Day Link Exploit 2024 is a recently discovered cybersecurity vulnerability that enables attackers to execute malicious code or gain unauthorized access through unpatched software flaws. This exploit poses a critical threat due to its ability to bypass conventional security defenses, putting organizations and individuals worldwide at risk.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4

What Is the Zero-Day Link Exploit?
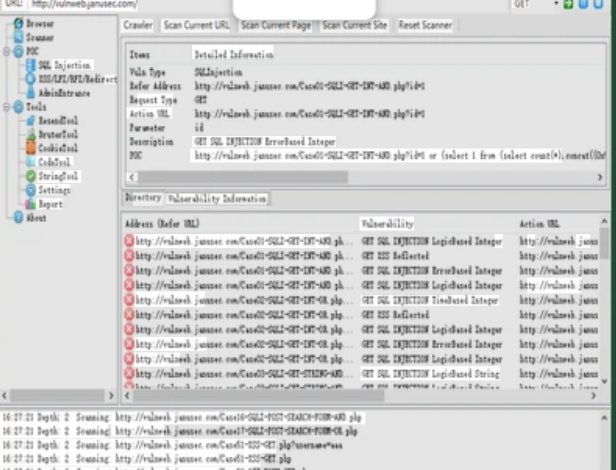
A zero-day exploit is a cyberattack that targets a previously unknown vulnerability in software or hardware before developers can issue a patch. The Zero-Day Link Exploit 2024 specifically targets hyperlinks or URL-based functions in various applications, allowing attackers to inject malicious payloads, execute remote code (RCE), or steal confidential information. This exploit often remains undetected by antivirus and intrusion detection systems until countermeasures are developed.
Detailed Features of the Zero-Day Link Exploit 2024
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Stealthy Execution | Operates without leaving footprints in system logs, complicating forensic investigations. |
| Cross-Platform Compatibility | Targets multiple operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux) and applications like browsers and email clients. |
| Phishing Integration | Works alongside social engineering tactics to deceive users into clicking malicious links. |
| Zero Interaction Required | Certain variants trigger the exploit automatically via drive-by downloads without user action. |
| Persistence Mechanisms | Installs backdoors or malware that remain active even after system restarts. |
| Polymorphic Code | Continuously changes its code structure to avoid signature-based detection methods. |
| Privilege Escalation | Gains elevated system privileges to enable further compromise and exploitation. |
Why Use the Zero-Day Link Exploit?
Data Theft: Extracts sensitive personal or corporate information.
Ransomware Deployment: Encrypts files and demands ransom payments.
Espionage: Used in state-sponsored attacks targeting government or military assets.
Botnet Recruitment: Enlists infected devices into large-scale cyberattack networks.