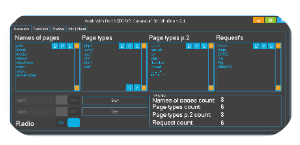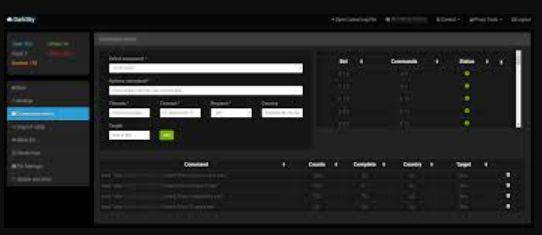
DarkSky DDoS Loader Bot Cracked 2025
DarkSky DDoS Loader Bot (DDoS) attacks persist as a significant threat to the cybersecurity landscape, disrupting services, extorting businesses, and resulting in substantial financial losses. Attackers often rely on powerful botnet tools to amplify their attacks, and one such tool, DarkSky DDoS Loader Bot Cracked 2025, has gained notoriety for its effectiveness and accessibility. This cracked version, leaked or distributed illegally, enables even low-skilled threat actors to launch devastating DDoS attacks without requiring advanced technical knowledge. Its role in modern cyberattacks ranges from hacktivism and competitive sabotage to ransomware-related extortion, making it a significant concern for organizations worldwide.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
What Is DarkSky DDoS Loader Bot and How Is It Used?
This software is a malicious botnet loader designed to recruit infected machines (bots) into a network controlled by an attacker. Once deployed, it enables large-scale DDoS attacks by flooding targets with overwhelming traffic, rendering websites or servers inaccessible. The “cracked” version refers to a modified version that bypasses licensing or authentication checks, making it widely available on underground forums and other unauthorized sources. Cybercriminals typically use it to:
- Launch volumetric attacks (UDP/ICMP floods).
- Execute protocol-based attacks (SYN floods, HTTP floods).
- Conduct application-layer attacks (Slowloris, DNS query floods).
- Rent out botnets as a service (DDoS-for-hire).
Key Features of DarkSky DDoS Loader Bot
| Feature | Description |
| Multi-Vector Attack Methods | Supports UDP, TCP, SYN, HTTP, and ICMP flood attacks. |
| Botnet Recruitment | Infects devices via malware droppers, turning them into attack nodes. |
| C2 (Command & Control) Server | Centralized control panel to manage bots and launch attacks. |
| Encrypted Communication | Uses AES or RSA encryption to evade detection by security tools. |
| IP Spoofing | Masks attack sources to complicate mitigation efforts. |
| Persistent Infection | Ensures bots remain active even after system reboots. |
| User-Friendly Interface | Simplifies attack configuration for less technical users. |
| Traffic Amplification | Leverages protocols like DNS, NTP, or Memcached for high-volume attacks. |
How the DarkSky DDoS Loader Bot
1. Infection & Bot Recruitment
The attacker spreads the botnet loader through:
- Phishing emails with malicious attachments.
- Exploit kits target unpatched software vulnerabilities.
- Drive-by downloads from compromised websites.
- Cracked software bundles (standard in pirated apps).
Once executed, the malware:
- Injects itself into system processes to avoid detection.
- Contacts the C2 server to receive commands.
- Downloads additional payloads if needed (e.g., miners, ransomware).
2. Command & Control (C2) Communication
The infected machines (bots) periodically check in with the attacker’s C2 server, awaiting instructions. Communication is often encrypted to bypass network monitoring. The attacker can:
- Update attack methods to switch between UDP and TCP floods.
- Adjust attack duration and intensity.
- Target new victims dynamically.
3. Attack Execution
When the attacker initiates a DDoS attack, the bots receive the target’s IP address or domain name, along with the attack parameters. Common techniques include:
a. Volumetric Attacks (Layer 3/4)
- UDP Flood: Sends a high volume of UDP packets to random ports, forcing the target to respond with ICMP “Destination Unreachable” messages.
- ICMP Flood: Overwhelms the target with ping requests (smurf attack if IP spoofing is used).
- SYN Flood: Sends TCP SYN requests without completing the handshake, exhausting server resources.
b. Application-Layer Attacks (Layer 7)
- HTTP Flood: Sends legitimate-looking but resource-intensive HTTP requests (GET and POST) to overwhelm the target system.
- Slowloris: Opens multiple connections and keeps them open with partial requests, starving server resources.
c. Amplification Attacks
- DNS/NTP Amplification: Sends minor queries to open DNS/NTP servers with a spoofed source IP, triggering significant responses to the victim.
4. Evasion & Persistence
To avoid detection and removal:
- Kills security processes (antivirus, firewalls).
- Modifies registry entries for persistence.
- Uses domain generation algorithms (DGA) to bypass blocklisting.
- Rotates C2 IPS to prevent takedowns.
5. Post-Attack Actions
After an attack, the botnet may:
- Log successful attacks for future extortion.
- Self-update to include new exploits.
- Lie dormant until reactivated.
![Work With Dorks [DORK’s Generator]-Dork Generator](https://blackhatus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Work-With-Dorks-DORKs-Generator-Dork-Generator-1.png)