Gomorrah Stealr 4.0 Cracked
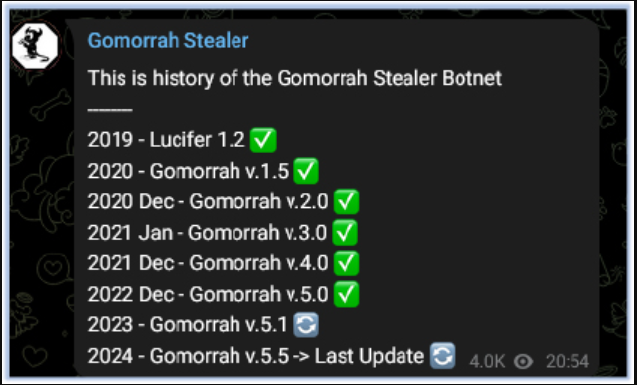
Information stealers have become one of the most pervasive threats in the cybercrime landscape, enabling attackers to harvest sensitive data for financial gain or further exploitation. Cracked or pirated versions of such malware, often distributed through underground forums, lower the barrier to entry for aspiring cybercriminals. The latest iteration of Gomorrah Stealr 4.0 demonstrates improved evasion techniques and expanded data-gathering capabilities, making it a significant risk to individuals and organizations alike.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
This software is a sophisticated information stealer designed to extract a wide range of sensitive data from infected systems. Typically distributed as a cracked or “free” version of legitimate software, it tricks users into executing the malware, which then operates silently in the background. Once active, it targets credentials, financial information, cryptocurrency wallets, and other valuable data, exfiltrating everything to attacker-controlled servers. Cybercriminals use this stolen information for identity theft, financial fraud, or selling it on dark web marketplaces.

Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Credential Theft | Extracts saved logins from browsers, email clients, and FTP applications. |
| Cryptocurrency Wallet Targeting | Scans for and steals wallet files (e.g., Exodus, Electrum, MetaMask). |
| System Data Collection | Gathers OS details, hardware specs, network information, and installed software. |
| File Grabber | Searches for and uploads specific file types (e.g., documents, databases). |
| Anti-Analysis Techniques | Uses obfuscation, VM/sandbox detection, and process injection to evade detection. |
| Persistence Mechanisms | Maintains access via registry modifications, startup entries, or task scheduling. |
| C2 Communication | Exfiltrates data via encrypted channels to a remote server. |
How Gomorrah Stealr 4.0 Works
Infection and Initial Execution
The malware is commonly distributed through:
- Pirated Software & Keygens: Disguised as cracked versions of popular paid programs.
- Fake Game Mods/Cheats: Bundled with downloads from untrusted sources.
- Phishing Campaigns: Malicious email attachments or fake update installers.
Once executed, the malware may use a multi-stage deployment process:
- Dropper Component: A seemingly harmless file (e.g., a game crack) extracts and executes the malicious payload.
- Anti-Detection Checks: The malware checks for virtual machines, debuggers, or security tools before proceeding.
- Persistence Setup: It ensures long-term access by modifying registry keys or creating scheduled tasks.
Data Harvesting Process
After establishing persistence, the malware begins scanning the system for valuable data:
- Browser Data Extraction: Targets Chromium-based browsers (Chrome, Edge, Brave) and Firefox, stealing saved passwords, cookies, and autofill data.
- Cryptocurrency Theft: Scans directories for wallet files (e.g., wallet.dat, MetaMask seed phrases) and uploads them.
- File Exfiltration: Searches for documents (PDF, DOCX, XLSX), databases, and configuration files in user directories.
- Clipboard Monitoring: Logs copied text to capture cryptocurrency addresses during transactions.
Evasion and Anti-Forensics
To avoid detection:
- Code Obfuscation: Uses encryption and junk code to hinder static analysis.
- Process Hollowing: Injects malicious code into legitimate processes (e.g., svchost.exe).
- Delayed Execution: Some variants wait before activating to bypass sandbox analysis.
Command and Control (C2) Communication
Stolen data is compressed, encrypted, and sent to the attacker’s server via:
- HTTPS POST Requests: Blends in with normal web traffic.
- Discord Webhooks or Telegram Bots: Some variants use messaging platforms for data exfiltration.
Tor-Based Servers: Advanced versions route traffic through anonymity networks.


