Rafel Rat 2025
In recent years, cybercriminals have increasingly relied on sophisticated tools to carry out attacks, with one notable example being a particular remote access trojan (RAT) that has gained notoriety in underground forums. Rafel Rat 2025 malware, often distributed through cracked or pirated software, enables attackers to gain complete control over compromised systems. Its modular design and evasion techniques make it a persistent threat in modern cyberattacks, particularly in credential theft, espionage, and ransomware deployment.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4
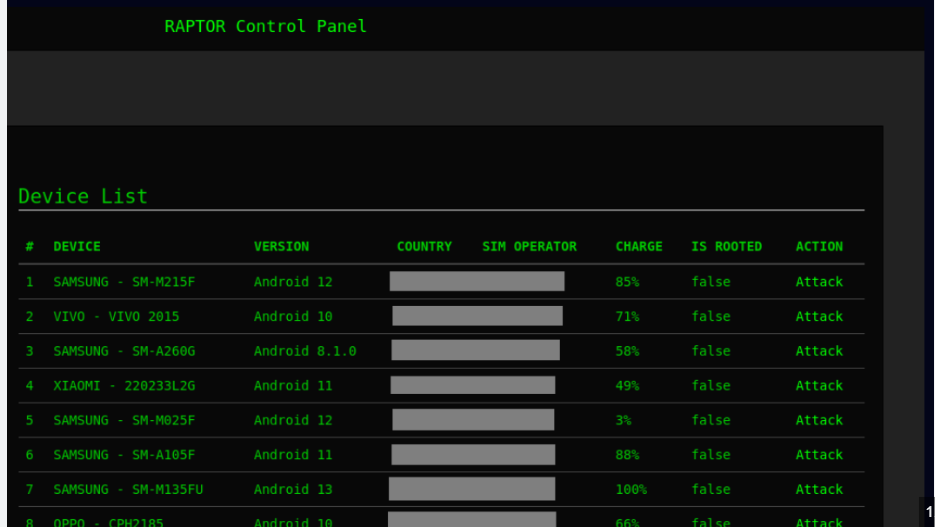
This software is a powerful remote administration tool that, when used maliciously, can function as a remote access tool (RAT). Legitimate versions are marketed for remote system management, but threat actors repurpose cracked variants for unauthorized access. It provides extensive control over infected machines, including keystroke logging, screen capture, file exfiltration, and even webcam activation. Attackers typically distribute it via phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploit kits, often disguised as legitimate software or bundled with pirated applications.
Key Features of Rafel Rat 2025
| Feature | Description |
| Remote Access | Allows attackers to remotely control the victim’s system. |
| Keylogging | Captures keystrokes to steal credentials and sensitive data. |
| Screen Capture | Takes screenshots of the victim’s desktop activity. |
| File Manipulation | Enables file upload, download, deletion, or encryption. |
| Persistence Mechanisms | Ensures the malware remains active after system reboots. |
| Evasion Techniques | Uses obfuscation, anti-VM checks, and code injection to avoid detection. |
| Payload Delivery | Deploys additional malware, such as ransomware or spyware. |
How Rafel Rat 2025 Works
Infection and Execution
The malware typically infiltrates a system through social engineering, such as a malicious email attachment or a fake software installer. Once executed, it establishes persistence by modifying registry keys or creating scheduled tasks. Some variants employ process hollowing—a technique in which a legitimate process (e.g., explorer.exe) is hijacked to execute malicious code, thereby making detection more challenging.
Communication and Command Control (C2)
After installation, the malware connects to a command-and-control (C2) server, often using encrypted protocols such as HTTPS or DNS tunnelling to evade network monitoring. The C2 server sends instructions, which the malware executes on the victim’s machine. This two-way communication allows real-time control.
Payload Delivery and Functionality
The malware’s modular design enables attackers to deploy additional payloads as needed. Common techniques include:
- DLL Injection: Injects malicious code into legitimate processes to avoid detection.
- Living-off-the-Land (Lotl): Uses built-in system tools (e.g., PowerShell or WMI) for malicious activities.
- Data Exfiltration: Compresses and transmits stolen data to the attacker’s server.
Evasion Techniques of Rafel Rat 2025
To bypass security solutions, the malware employs:
- Code Obfuscation: Makes analysis difficult by scrambling its code.
- Anti-Sandbox Checks: Detects virtual environments and halts execution to prevent analysis and exploitation.
- Rootkit Capabilities: Hides its presence by manipulating system APIS.
Once fully deployed, the malware enables attackers to conduct extensive surveillance, steal data, or further exploit the network. Its adaptability and stealth make it a significant threat in targeted attacks.


