BTC Stealer 2025
Cybercriminals have developed specialized tools to exploit digital asset holders as cryptocurrency adoption grows. Among these threats is a malicious software category designed to steal cryptocurrency wallets and credentials, commonly called BTC Stealer 2025 in underground forums. This type of malware has become increasingly prevalent in attacks targeting both individual investors and exchanges, often leading to significant financial losses. Its ability to bypass security measures and operate stealthily makes it a persistent threat in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Download Link 1
Download Link 2
Download Link 3
Download Link 4

Overview of BTC Stealer 2025
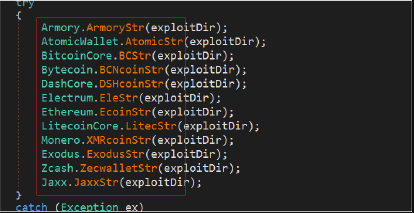
This software is a type of malware specifically engineered to locate and exfiltrate cryptocurrency-related data from infected systems. It primarily targets wallet files, browser-stored credentials, and clipboard contents (to hijack transactions). The malware is typically distributed through phishing campaigns, fake cryptocurrency apps, or bundled with pirated software. Once executed, it scans the system for valuable data and sends it to a remote server controlled by the attacker. Cybercriminals often use this tool in combination with other malware, such as keyloggers or infostealers, to maximize their theft potential.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
| Wallet Detection | Scans for and steals cryptocurrency wallet files (e.g., wallet.dat). |
| Browser Targeting | Extracts saved credentials from wallets like MetaMask and Coinbase. |
| Clipboard Hijacking | Monitors and alters copied cryptocurrency addresses during transactions. |
| Auto-Exfiltration | Automatically sends stolen data to a C2 server via encrypted channels. |
| Persistence | Maintains access via registry modifications or scheduled tasks. |
| Evasion Techniques | Uses obfuscation and process injection to avoid detection. |
| Multi-Currency Support | Targets Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other popular cryptocurrencies. |
How the Software Works
The malware operates through a series of stages designed to maximize theft while minimizing detection:
1. Delivery & Initial Infection
- Phishing Emails.
- Fake Crypto Apps.
- Exploit Kits.
- Pirated Software.
Once executed, the malware checks for:
- Virtualization/Sandboxing.
- Security Software.
2. Data Harvesting
- Wallet Files.
- Browser Data.
- Clipboard Contents.
3. Exfiltration & C2 Communication
- Encrypted HTTPS Requests.
- DNS Tunneling.
- Decentralized Storage.
4. Persistence & Evasion
- Registry Modifications.
- DLL Injection.
- Timestamp Spoofing.


